激酶实验
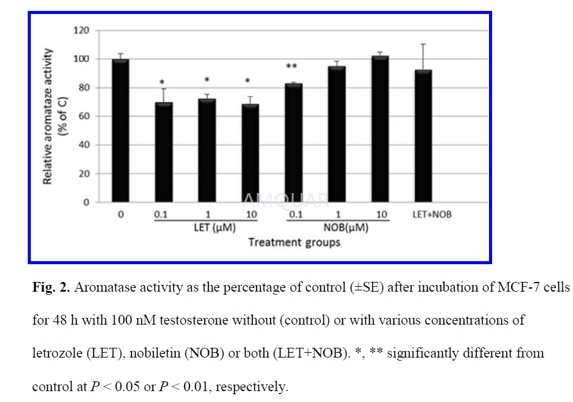
Aromatase activity assay[1]
Aromatase enzyme activity was determined incell cultures by measuring the conversion of androgenic substrate testosterone(T) into E2.
Cells were counted and plated at a densityof 3 × 105 cells/well in medium containing 5% FBS. After 24 h,culture medium was removed and replaced by 2% DCC FBS phenol red-free RPMImedium containing the aromatase substrate T (100 nM) and with either vehicle(0.1% DMSO), or various concentrations (0.1, 1, 10μM) of NOB, LET, orcombination of LET (1μM) and NOB(1μM). After 48 h incubation, the media werecollected and stored at –20°C until further analysis. E2 concentrations weremeasured using an electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) kit by elecsys2010 instrument with sensitivity 18.4pmol/L, an intra-assay coefficient ofvariation of 1.9–5.7%, and an inter-assay coefficient of variation of 2.3–6.2%.
Protein concentrations were determined bythe Bradford method, with bovine serum albumin as standard. Aromatase activitywas calculated as picograms of E2 synthesized per hour per milligram protein(pg E2/hour/mg protein) and expressed as percentage of control.
细胞实验
Cell culture andtreatment[1]
Wild-type human breast cancer MCF-7 cellswere cultured in RPMI-1640, supplemented with 10% FBS, 1%penicillin-streptomycin at 37 oC in a humidifiedincubator with 5% CO2. The medium was replaced every 2 days andcells were routinely subcultured when 80% confluence was reached. Cells wereharvested using trypsin-EDTA. Cell number and viability were determined bystaining a small volume of cell suspension with 0.4% trypan blue saline solution.MCF-7 cells were plated onto 96-well plates (MTT assay) or 6-well plates (aromataseactivity and mRNA expression).
Nobiletin (NOB) and LET were prepared as1000× stock solutions in DMSO and stored at −70oC. Different concentrations were added freshly to themedium while the concentration of DMSO was limited to 0.1% v/v. Cells weretreated with either the test compounds or the vehicle (0.1%, v/v DMSO) asnegative control. Each treatment was tested in duplicate; each experiment wasrepeated at least three times.
MTTassay for cell viability
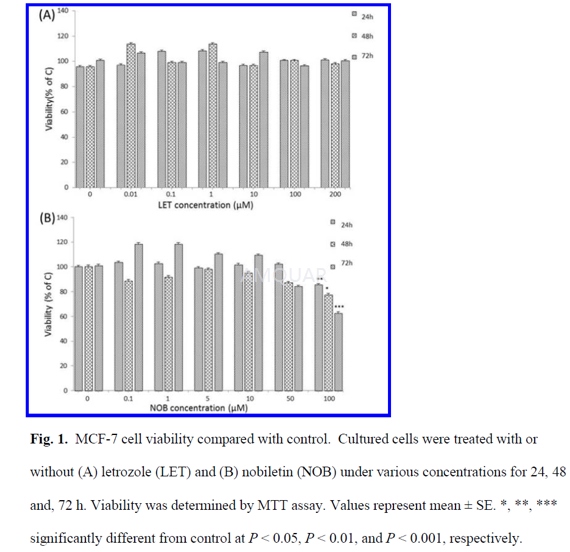
MTT assay, the capacity of MCF-7 cells toreduce MTT to formazan, was used to examine cytotoxicity in response to NOBand/or LET treatment.
Cells were seeded in 96-well plates at adensity of 5000 cells/well. After one day, the medium was replaced withphenol-red free RPMI medium supplemented with 2% dextran-coated charcoal-strippedFBS (DCC-FBS) and incubated overnight. Cells were treated with various concentrationsof LET and NOB and were incubated for 24, 48, and 72 h in the absence or presenceof the tested compounds. After the incubation period, the medium was removed,and
100μL of a 5mg/mL solution of MTT were added to each well and the cells were incubated for3h at 37°C. Then MTT-containing media was aspirated and 100μLDMSO was added to each well and the plates were incubated for 10 min at roomtemperature. The absorbance (A) was measured in the wavelength range of 570 -630 nm using a plate reader. Cell viabilities were calculated by the followingformula: Viability (%) = (Atreated/Acontrol) x 100%.
动物实验
Animals and letrozole (LET) administration[2]
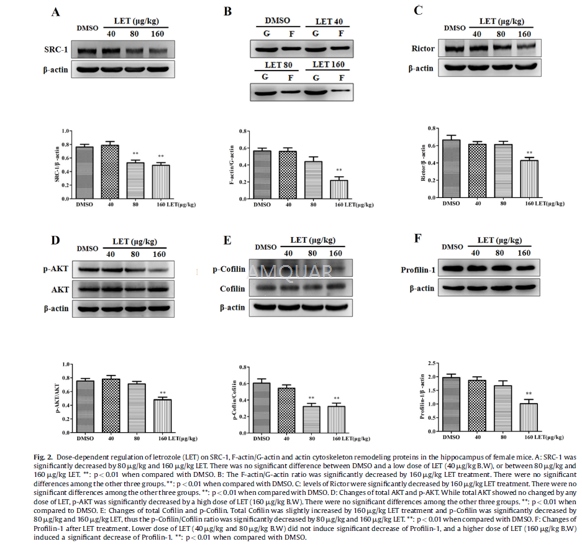
Different postnatal (P0-P56) male andfemale and adult (12 weeks old, 20±2 g) femaleSPF grade C57BL/6 mice were obtained. LET was dissolved in DMSO and dilutedwith sterile saline solution before injection. Adult female SPF grade C57BL/6mice were randomly divided into four groups. The LET groups wereintraperitoneally injected with LET in doses of 40 mg/kg, 80 mg/kg and 160mg/kg body weight (100 ml/each mouse), respectively. The control animals wereinjected intraperitoneally with vehicle solution (2% DMSO + 98% sterile salinesolution; 100 ml/each mouse). The injection was conducted every morning andlasted for 1 week. At day 7, all of the animals were killed for furtherexperiments.
SRC-1RNA interference lentivirus preparation
For lentiviral gene transfection,lentiviruses that expressed enhanced GFP and SRC-1 under the control of thepLentis-EF-GFP- miR-PGK-PURO parent vector were used. To make the SRC-1 shRNAcompatible with multiple viral vectors, a ligase was used to insert the shRNAinto the PSTI site of the vectors. Three SRC-1 shRNAs were designed and tested;the sequences of these shRNAs were as follows:
shRNA-1:
sense: TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGCGCCCATCCTATAGATTCATATTAGTGAAGCCAC;
antisense:AGATGTAATATGAATCTATAGGATGGGCTTGCCTACTGCCTCGGA.
shRNA-2: sense: TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGACCTCTTTAAACCTCAATAATTTAGTGAAGCCA;
antisense:CAGATGTAAATTATTGAGGTTTAAAGAGGGTGCCTACTGCCTCGGA.
shRNA-3: sense:TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGCGCAGATTGCCTGAACTAGAATTAGTGAAGCCA;
antisense:CAGATGTAATTCTAGTTCAGGCAATCTGCTTGCC- TACTGCCTCGGA.
The human elongation factor-1 alpha (EF-1α)promoter and the SRC-1 shRNA were cloned into the XhoI/EcoRI site of thevectors. Because the three SRC-1 shRNAs produced similar interference efficacyin 293T cells, we selected shRNA-1 (referred to as shSRC-1) for use insubsequent experiments.
For viral particle production, HEK 293T/17cells were grown in DMEM/10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and plated in 10-cmdishes at a density of 3 x 106cells/dish. The day after plating, thecells were transfected with SRC-1 shRNA plasmids using calcium phosphate asfollows: 1.5 mg pMD2G, 4.5 mg psPAX2, and 6 mg multiple viral vectors. Theconditioned medium was collected 48 h after transfection and immediately frozenfor the preparation of SRC-1-containing particles. For the second harvest ofviral particles, which took place on the next day, DMEM was replaced with freshmedium. The supernatant was clarified by filtering it through a 0.45-mm filterand was ultracentrifuged at 4oC for 120 min at 50,000g. The pelletwas resuspended in 100 ml PBS and left standing at 4 oCfor 30 min. Viral titer, in transducing units (TU)/ml, was determined using ahuman immunodeficiency virus (HIV) p24 ELISA kit and a Lentivirus Quantitationkit in HEK-293T cells; and the final titer was 1.5 x109 TU/ml.
Westernblot analysis
The hippocampus of the mice or frommHippoE-14 cells were lysed, membranes were blocked with 5% milk-TBST and thenincubated with the individual diluted primary antibodies at 4oCovernight. After several washes, the membranes were incubated withHRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (1:2000) or goat anti-mousesecondary antibodies (1:2000). The blots were finally visualized withchemiluminescent HRP substrateby Western Lightning- ECL. For phospho-AKT(Ser473)/AKT or phospho-Cofilin (Ser3)/Cofilin measurement, the twophospho-proteins were examined first with the protocol as mentioned above, thenthe membranes were washed with a specific stripping buffer, blocked with 5%fresh-prepared milk, incubated with the diluted individual primary antibodiesagainst AKT or Cofilin, and then, the process continued to the next step. Theoptical density for each band was measured using Quantity One software andnormalized to that of b-actin or corresponding total proteins. A blank control(without the primary antibody) was used to determine the specificity of theprimary antibodies and a pre-stained protein marker was employed to localizethe specific band of the primary antibodies. The antibodies were as follows:mouse monoclonal anti-aromatase (1:500); rabbit polyclonal anti-SRC-1 (1:600),rabbit mAb-Rictor (1:500), rabbit mAb-phospho-AKT (Ser473) (1:2000), rabbitmAb-Akt (1:1000), rabbit monoclonal actin antibody (1:2000), rabbitmAb-phospho-Cofilin (Ser3) (1:300), rabbit mAb-Cofilin (1:300), rabbitpolyclonal anti-Profilin-1 (1:4000), and mouse mAb-β-actin(1:1000).
F-actin/G-actinratio measurement
The F-actin to G-actin ratio was determinedby Western blotting. Briefly, the hippocampus was isolated and homogenized incold lyses buffer (10 mM K2HPO4, 100 mM NaF, 50 mM KCl, 2mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 0.2 mM dithiothreitol, 0.5% Triton X-100, 1 Msucrose, pH 7.0) and then centrifuged at 15,000g for 30 min. G-actin (solubleactin) was measured in the supernatant with a rabbit monoclonal actin antibody.To measure F-actin, the pellets were resuspended in an equal volume of lysesbuffer (1.5 mM guanidine hydrochloride, 1 mM sodium acetate, 1 mM CaCl2,1 mM ATP, 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH7.5) and incubated on ice for 1 h to depolymerizeF-actin with gentle shaking every 15 min. The samples were centrifuged at15000gfor 30 min, and this supernatant was used to measure actin (as a reflection ofinsoluble F-actin) with the same rabbit monoclonal actin antibody. Samples fromthe supernatant (G-actin) and pellet (F-actin) fractions were proportionallyloaded and analyzed with Western blot as mentioned above.