Autophagy
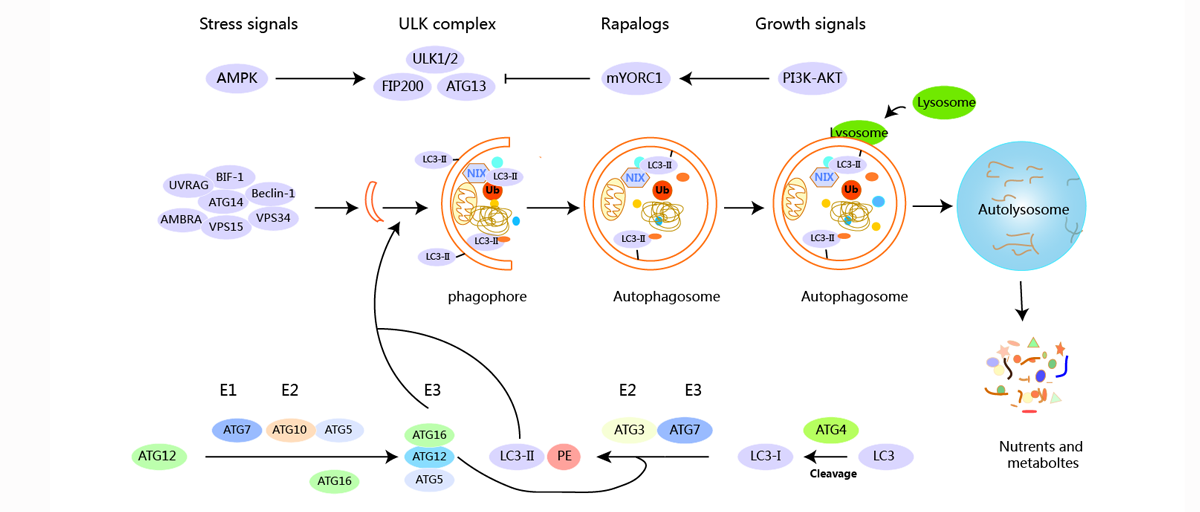
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis) is the natural, regulated, destructive mechanism of the cell that disassembles unnecessary or dysfunctional components.
Autophagy allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. In macroautophagy, targeted cytoplasmic constituents are isolated from the rest of the cell within a double-membraned vesicle known as an autophagosome. The autophagosome eventually fuses with lysosomes and the contents are degraded and recycled. In disease, autophagy has been seen as an adaptive response to stress, which promotes survival, whereas in other cases it appears to promote cell death and morbidity. In the extreme case of starvation, the breakdown of cellular components promotes cellular survival by maintaining cellular energy levels.