-
生物活性
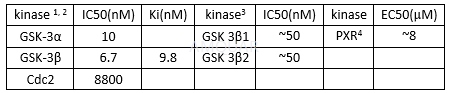
CHIR-99021 (CT99021),a cell permeable, ATP-competitive small organic molecule, highly specific inhibitsGSK3 activity and activates Wnt/β- catenin signaling as well. CHIR-99021 is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) (IC50 values are 6.7 and 10 nM for GSK-3β and GSK-3α respectively). CHIR-99021 exhibits little to no activity toward 46 other enzymes (IC50 >8.8 μM against 20 kinases and Ki ≥5 μM against 23 non-kinase enzymes) and shows only weak binding to 22 pharmacologically relevant receptors (Kd ~4 μM). Exhibits >500-fold selectivity for GSK-3 over closely related kinases; also displays >800-fold selectivity against 45 additional enzymes and receptors.
CHIR-99021 stimulates GS activity in CHO-IR cells with an EC50of 763nM. [1]
Kinase activities of CHIR-99021
Cytotoxicity of CHIR-99021
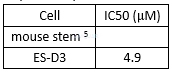
CHIR-99021 induces Brachyury-positive in ES-D3 cells with an EC50 of 3.19μM.[5]
CHIR-99021attenuates IL-1-induced eotaxin release by airway smooth muscle cells with anEC50 of 0.68 ± 0.04μM.[6]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
Optimisation of substrate priming andcharacterisation of purified GSK3 activity[3]
Kinase assays contained a mixture ofpurified kinase, protein or peptide substrate (final concentrations indicatedin figure legends), 10mM MgCl2, 0.1mM [γ-32P] ATP (approximately 106cpm/nmol) and kinase buffer [50mMTris–HCl, 0.03% (v/v) Brij-35, 0.1% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol,pH 7.4]. All assays were performed at 30 ℃ with shaking for thetimes indicated in text or figure legends. Reactions were terminated in one oftwo ways; either by precipitation by addition of trichloroacetic acid (finalconcentration20% v/v in the presence of 50μg bovineserum albumin), or by adsorption onto 2cm2 of p81 paper. Phosphateincorporation into substrate was measured by Scintillation counting. One unitof kinase activity is defined as that amount catalysing the incorporation of 1nmol of phosphate into peptide substrate in 1min (specific activity).
LinkedGSK3 assays
Substrate priming was carried out usingnon-radiolabeled MgATP as above, for the times established to result in maximalpriming. Subsequently, GSK3β was added along with additional MgCl2 and ATP ([γ-32P]106cpm/nmol) to a final concentration of 10mM and0.1mM respectively,for the times indicated. Reactions were terminated by addition of 4 x sodium dodecylsulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) loading buffer, proteinsseparated by SDS–PAGE (4–12% Novex gels) and visualised by Coomassie staining. Substrateproteins were excised from the gel and the phosphate incorporation assessed by Scintillationcounting.
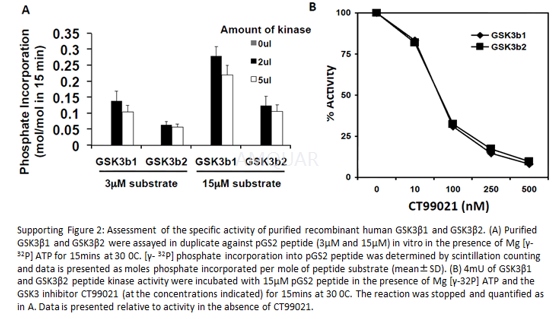
-
细胞实验
Mouse ES cell culture[5]
To maintain the pluripotency of the mouseES cell lines ES-D3 and ES-CCE, they were routinely cultured on gelatine-coateddishes in KO-DMEM containing 25mM glucose supplemented with 15% FCS, 2mM L-glutamine,100μM NEAA, 100μM 2-mercaptoethanol, penicillin/streptomycin, and 1,000 U/mlLIF. The medium was changed daily and the cells were passaged 2–3 times perweek. The basal medium for the comparative experiments was RPMI advancedsupplemented with 0.2% FCS, penicillin/streptomycin and 1-fold glutamax withdifferent concentrations of BIO, SB-216763, CHIR-99021 and CHIR-98014. A randomizedcontrol was performed with basal medium without growth factors and/or smallmolecules. Physiological activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin-pathway was testedin medium supplemented with 50ng/ml Wnt3a.
Cellviability assay
The viability of the mouse ES cells wasdetermined after exposure to different concentrations of GSK3 inhibitors forthree days using the MTT assay. The decrease of MTT activity is a reliablemetabolism-based test for quantifying cell viability; this decrease correlateswith the loss of cell viability. 2,000 cells were seeded overnight ongelatine-coated 96-well plates in LIF-containing ES cell medium. On the nextday the medium was changed to medium devoid of LIF and with reduced serum and supplementedwith 0.1 – 1μM BIO, or 1 – 10μM SB-216763, CHIR-99021 orCHIR-98014. Basal medium without GSK3 inhibitors or DMSO was used as control. Alltested conditions were analyzed in triplicates.
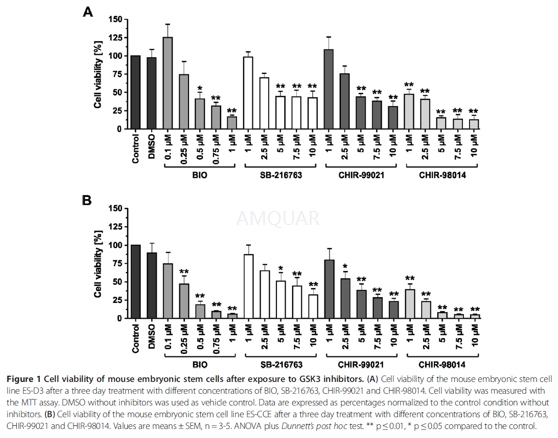
-
动物实验
Animal experiments[7]
Sixteen male C57BL6/J background micebetween 17 and 24 weeks of age were housed under controlled temperature (22 ℃),humidity (40%) and light (12 h:12 h light/dark cycle) conditions in a specificpathogen-free vivarium and provided food and water ad libitum. All experimentalprocedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.For 3 consecutive days, mice were injected intraperitoneally with either 7.5mg/kg per day CHIR 99021 (45% saline, 45% PEG400, 10% DMSO) or saline/PEG400.Following the injection on the third day, the mice were anaesthetized withinhaled isoflurane and killed by cervical dislocation. The thoracic aorta washarvested and periaortic fat removed with the use of a dissecting microscope, onice. The aortas were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 ℃. For western blot analysis, aortas werehomogenized in a tissue grinder in a Triton-based buffer containing 20mM TrispH 7.5, 150mM NaCl, 1mM EDTA, 1mM EGTA, 0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 2.5mM sodiumpyrophosphate, 1mM β-glycerophosphate, 1mM sodium orthovanadate and 1μg/ml leupeptin.Following brief sonication, lysates were centrifuged at 16,300 g for 10 min at4 ℃. The supernatants were stored at −80 ℃ for future analysis.Protein levels were analysed in these samples by western blot. During theseanalyses, GAPDH was overexposed so we utilized a loading control located in adifferent region of the membrane, Hsp90.
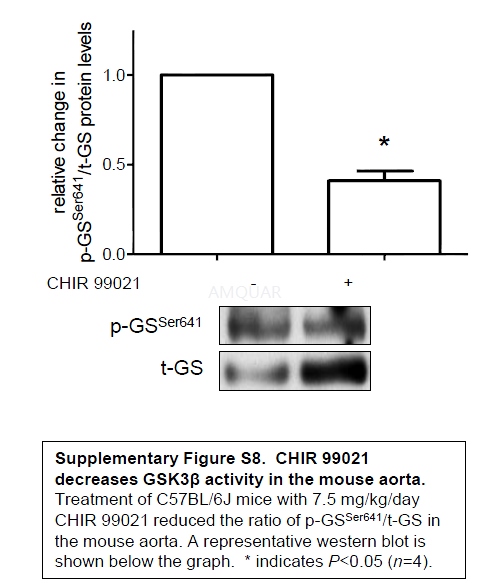
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Ring DB JK, Henriksen EJ, Nuss JM, Goff D, Kinnick TR, Ma ST, Reeder JW, Samuels I, Slabiak T, Wagman AS, Hammond ME, Harrison SD. Selective glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors potentiate insulin activation of glucose transport and utilization in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2003;52(3):588-595.
[2] Bennett CN, Ross SE, Longo KA, et al. Regulation of Wnt signaling during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(34):30998-31004.
[3] Soutar MP, Kim WY, Williamson R, et al. Evidence that glycogen synthase kinase-3 isoforms have distinct substrate preference in the brain. J Neurochem. 2010;115(4):974-983.
[more]
分子式
C22H18Cl2N8 |
分子量
465.34 |
CAS号
252917-06-9 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
10 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们