-
生物活性
KN-93 Phosphate is CaM kinase II inhibitor; water soluble version of KN 93. KN-93 H3PO4, the phosphate-saltform of KN-93, is a potent, specific calmodulin-competitive inhibitor of CaMKII.
KN93inhibits of IKr with an IC50 of 102.57 ± 9.28 nM. [1]
KN-93directly blocks the Kv1.5 Channel with an IC50 of 307 ± 12 nM. [2]
KN-93 inhibits CaMKII activity with a Ki value of 0.37μM. [3]
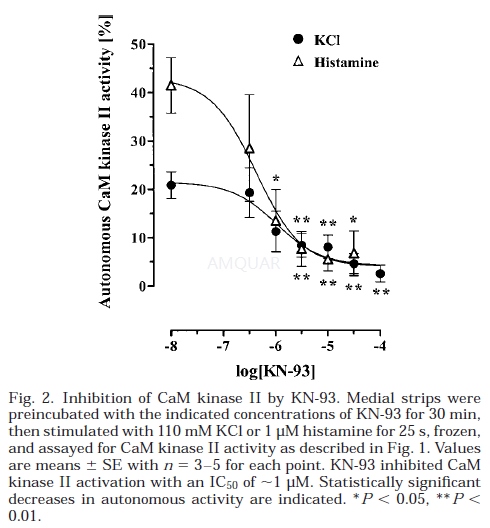
KN-93inhibited CaM kinase II activation with an IC50 of ~1 μM. [4]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
4 微升包含 0.02% 抗坏血酸的 0.9% 生理盐水
-
激酶实验
Chemicals[4]
KN-93 was dissolved in deionized H2O or in DMSO.
CaMkinase II activity assay
Activation of the kinase is inferredthrough an increase in the tissue extracts of Ca2+/calmodulin-independent(or ‘‘autonomous’’) activity assayed with a specific peptide substrate(autocamtide 2; KKALRRQETVDAL) of CaM kinase II. This increase in autonomous activityis dependent on a specific autophosphorylation event (threonine-287 in δ and γ-subunits) that occurs between Ca2+/ calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM)-activated subunits within the multimeric holoenzyme and is preservedduring extraction of the kinase from intact tissues by inclusion of phosphataseinhibitors.
Frozen tissues were stored in liquid N2,then pulverized in liquid N2-cooled stainless steel vials (CrescentDental) in the following solution: 50mM MOPS, 1% Nonidet P-40, 100mM sodiumpyrophosphate, 100mM NaF, 250mM NaCl, 3mM EGTA, 1mM 1,4-dithiothreitol (DTT),0.23 U/ml aprotinin, 0.1mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1μg/ml leupeptin, 2μg/mltrypsin inhibitor, and 2μM microcystin LR. Homogenates were thawed on ice andcentrifuged at 17,000g for 15min at 4°C. Autocamtide 2 kinase activity wasassayed in a total volume of 25μl containing 50mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 10mMmagnesium-acetate, 0.2mM [γ-32P] ATP (specific activity 440cpm/pmol), 20μMautocamtide 2, plus 1mM EGTA (for assay of autonomous, Ca2+/CaM-independentactivity) or 600nM calmodulin and 0.8 mM CaCl2 (for assay of total activity). Assayswere carried out at 30°C, started by the addition of lysate (2–4μg totalprotein), and stopped at 2min by spotting aliquots onto P-81 phosphocellulosepaper squares. P-81 papers were washed exhaustively in 75 mM phosphoric acid, followedby a wash in ethanol, then dried. Bound radioactivity was counted in a liquidscintillation counter. Protein concentrations were determined using the Lowrymethod. Total and autonomous CaM kinase II activities were calculated innanomoles of Pi incorporated in autocamtide 2 per minute per milligram lysateprotein. Autonomous activity, a measure of the activation state of CaM kinaseII, was reported as a percentage of total activity measured in the sameextract. Under these conditions, kinase activity assays were linear up to 7minand over a range of 0–6μg total protein/assay. To ensure that the reactionswere enzyme limited, the concentration of autocamtide 2 was set at a sixfoldexcess based on the highest measured kinase activity.
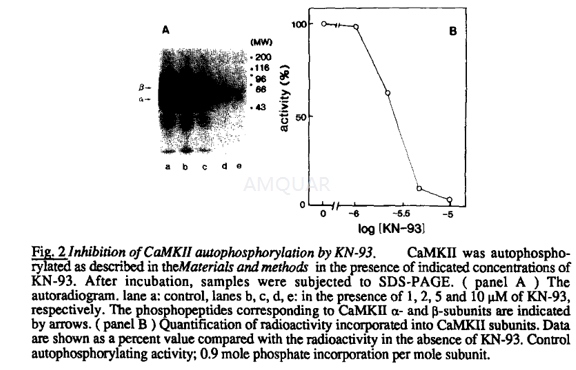
Measurement of activities of auto-phosphorylated/non-auto-phosphorylateCaMKII[3]
CaMKII activity was measured utilizingsyntideII as a substrate. Purified CaMKII was pre-incubated in the assay mixture( 35mM Hepes-Na ( pH 8.0 ), 10mM MgCl2,0.5μM CaM, 5μMATP, 1mM CaCl2 or 1mM EGTA, total 25μl at 30oCfor 2minutes. After this pre-incubation, the protein substrate/radioactive ATPmixture was added to the same test tube and the preparation was furtherincubated at 30oC, for 5minutes (final assay condition; 35mMHepes-Na (pH 8.0), 10mM MgCl2, 0.125μI CaM, 20μI syntideII, 11.25μM [γ-32P] ATP, 10% DMSO and indicated concentrations ofKN-93, supplemented with 0.25mM CaCl2 and 2mM EGTA (for auto-phosphorylatedsamples ) or 0.25mM EGTA and 2mM CaCl2 ( for non-auto-phosphorylatedsamples ), total 100μl ). The reaction was terminated by adding of 25μlof 100 % (w/v) ice-cold TCA. After centrifugation (12,000 x g, 4oC,10 min), 80μI of the supematant was applied to phosphocellulose paper. Thefilters were then washed with 75mM H3P04 for 15min withcontinuous agitation. After 4-cycles of washing, the radioactivity retained onthe filter paper was quantified in a liquid scintillation counter.
-
细胞实验
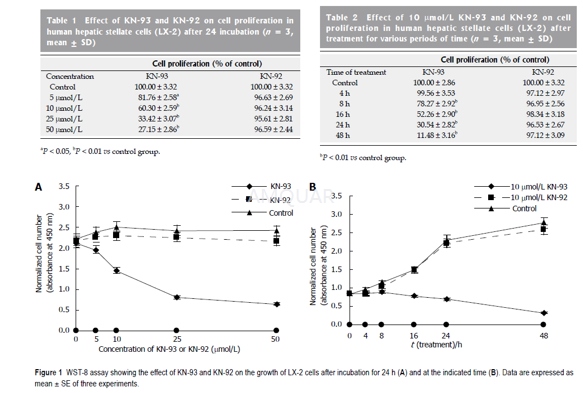
Cell line, culture conditions and KN-93treatment[5]
The human hepatic stellate cells werepropagated in DMEM supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum,penicillin (100U/mL) and streptomycin (100g/L) under standard culture conditions(37℃, 950mL/L humol/lidified air and 50 mL/L CO2). A stocksolution of 10mmol/L KN-93 and 10mmol/L KN-92 in DMSO was prepared, and finalconcentrations (1, 5, 10, 25, 50μmol/L) in DMEM were preparedfrom stock solution immediately before use. DMEM with an equal volume of DMSO servedas a negative control.
WST-8assay
The proliferation of LX-2 cells wasestimated by CCK-8 assay according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. LX-2 cellstreated with DMSO were used as a control. This assay is based on the cleavageof the tetrazolium salt WST-8 by mitochondrial dehydrogenase in viable cells.Briefly, LX-2 cells (2 × 103 cells/well) were incubated with 100μLof culture medium in 96-multiwell plates. After incubated with KN-93 or KN-92at indicated concentrations for 24h or with 10μmol/L ofKN-93 or KN-92 for indicated periods of time, the media were removed and 100μLof DMEM containing CCK-8 (10μL) was added to each well. After a further 2 hincubation at 37℃, the absorbance at 450nm of each well was measured with a Thermomaxmicroplate reader. Each experiment was repeated three times, and the datarepresent the mean of all measurements.
-
动物实验
Animals[6]
Ninety adult rats (Sprague Dawley femalesweighing 180–220g) were used in this study.
Experimentaldesign
As shown in Figure 1, 6-hydroxydopamine(OHDA) injections were used to produce a rat model of PD. After 3 weeks ofinjections, rats showing stable apomorphine-induced rotations (>7turns/minutes)were selected as valid PD rats. Forty valid PD rats were treated with levodopaplus benserazide twice daily for 21days. Abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs)scores were measured on days 1, 7, 14, and 21 of treatment. In addition, onegroup of PD rats (PD group, n = 10) and another group of sham-operated rats(sham group, n = 10) were treated with vehicle twice daily for 21 days. On day22, 40 levodopa-treated PD rats were randomly divided into four groups:levodopa + KN-93 (1μg) group, levodopa + KN-93 (2μg) group, levodopa + KN-93(5μg) group, and levodopa + vehicle group. These rats were intrastriatallytreated with different doses of KN-93 (1μg, 2μg, or 5μg) or vehicle beforelevodopa treatment, respectively. As a control, the sham group and PD grouprats received intrastriatal administration of vehicle before vehicle treatment.Apomorphine-induced rotations were measured to observe the antiparkinsonianeffect of KN-93 on day 1 and day 22. AIMs scores were measured to observe theantidyskinetic effect of KN-93 in rats on days of 1, 7, 14, 21, and 22. By theend of the experiment, rats were sacrificed by deep anesthesia using 3%phenobarbital. Western blot was used to determine levels of GluR1 andpGluR1S845 in rats. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used tomeasure levels of Gad1 and Nurr77 in rats.

-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Hegyi B, Chen-Izu Y, Jian Z, Shimkunas R, Izu LT, Banyasz T. KN-93 inhibits IKr in mammalian cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;89(Pt B):173-176.
[2] Rezazadeh S, Claydon TW, Fedida D. KN-93 (2-[N-(2-hydroxyethyl)]-N-(4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl)]amino-N-(4-chlorocinnamyl)-N -methylbenzylamine), a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor, is a direct extracellular blocker of voltage-gated potassium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;317(1):292-299.
[3] Sumi M KK, Ishikawa T, Ishii A, Hagiwara M, Nagatsu T, Hidaka H. The newly synthesized selective Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II inhibitor KN-93 reduces dopamine contents in PC12h cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;181(3):968-975.
[more]
分子式
C26H29ClN2O4S.H3O4P |
分子量
599.03 |
CAS号
1188890-41-6 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
100 mg/mL |
Water
90 mg/mL |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们