-
生物活性
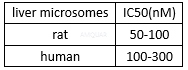
Simvastatin is an HMGCR (HMG-CoA reductase) inhibitor with anti-proliferative properties. This compound has been shown to modulate purified bovine pituitary 20 S proteasome via mild stimulation of chymotrypsin-like activity and inhibition of peptidylglutamylpeptide hydrolyzing activity. Has multiple biological effects including bone formation stimulation, inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, and anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity. Mechanistic studies suggest that Simvastatin decreases CDK4 and CDK2 kinase activities and represses high glucose-induced Rho A (Rho GTPase)/p21 signaling in mesangial cells. Simvastatin also potentiates apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells via the suppression of TNF-induced NF-κB activation (IC50 ~ 13 µM). Simvastatin(MK-733), a lipophilic inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase with anti-inflammatory,antiatherosclerotic, and antioxidant effects, is mainly used to regulatecholesterol synthesis in patients with increased risk of cardiovascularcomplications.
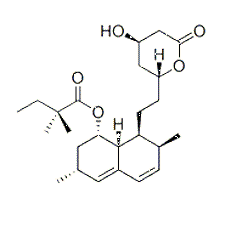
HMG-CoAreductase activity of Simvastatin[1]
HMG-CoA reductase activity of simvastatin
Simvastatininhibits the migration response induced by PDGF with an IC50 value of 2μM.[5]
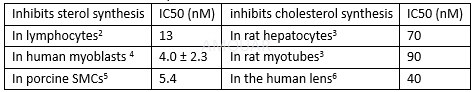
Inhibitoryeffect of simvastatin on mitochondrial respiration[7]
Growth inhibition of simvastatin
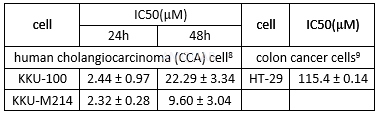
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
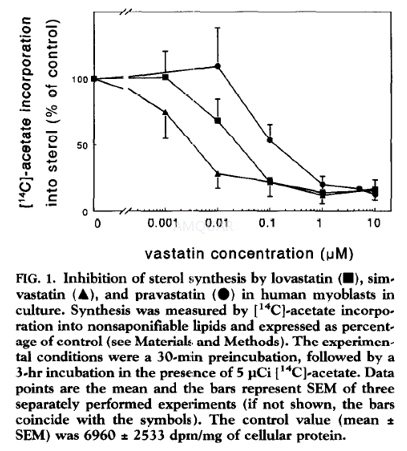
Determination of Sterol Synthesis[4]
Human myoblasts (in 10 cm2 wells) were preincubated for 30 min in the absence or presence of 0.001, 0.01,0.1, 1 .0 and 10μM of simvastatin in medium supplemented with 20%lipoprotein-deficient serum. Cells were incubated further for 3hr with 5μCi[14C]-acetate (specific radioactivity of 56.2 mCi/mmol) per well. [14C]-acetateincorporation into sterols was measured.
Samples were taken for protein determination.Nonsaponifiable lipids were separated by using thin layer chromatography systemI. To calculate the IC50 values of simvastatin curve fitting through all datapoints using a dose-response equation was performed. Sterol synthesis was alsomeasured in cells preincubated for 2 days with 0, 0.1, and 1μMof simvastatin and further incubated for 24hr in the presence of 5μCiof [14C]-acetate per well.
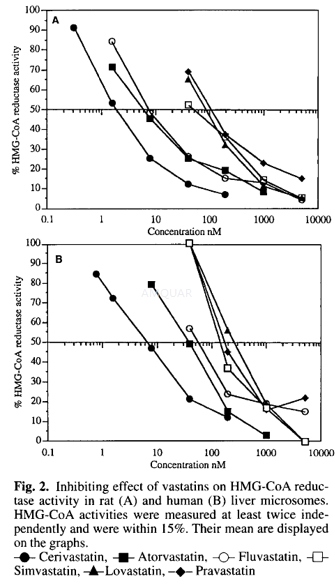
HMG-CoA reductase activity[1]
HMG-CoA reductase activity was measured using modifications of the assay. The total volume ofeach assay was 95μI and the reaction mixture contained 10μI of theinhibiting compound to be tested and 85μI of theincubating buffer containing 2mg/ml liver microsomes, 0.1M KH2P04,pH 7.2, 5.7mM dithiothreitol, 10mM glucose-6-phosphate, 2U/mlglucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, 1mM NADP, 10μM miconazole.Control experiments were done without NADPH generating system. All samples wereincubated 10 min at 37°C before addition of 5μI ofsubstrate (unlabelled and 14C-HMG-3-hydroxy3- methyl glutaryl CoA,final concentration 50μM, 2.5nCi/nmole). After 30 min at 37OC, the reaction was stoppedby adding 27μI 1N HCl and 20μI of unlabelled mevalonolactone (200μg/assay). Theconversion of mevalonic acid to lactone was performed at room temperature for60 min.
One hundredμI of theassay were applicated to a 2ml column containing 100-200 mesh AG 1X8 CI form. Mevalonolactonewas eluted with 4 x 500μI of H2O. The eluates were mixed with 6 ml of Pico-Fluor40. The radioactivity of the samples was counted in a Packard Tricarbscintillation counter with automatic quenching correction. IC50 values wereobtained by plotting the percentage of activity against test compoundconcentration.
The same experiment done with an internalstandard (3H-mevalonolactone) has indicated that the percentage of recoverywas 80% ± 10%. Control experiment checking the formation of mevalonolactone wasrealized spotting directly40μI of the incubation mixture onto Silica Gel thinlayer plates and thechromatogram was developed in acetone:cyclohexane (1: 1, vol./vol.). Theradioactivity profile was analysed and quantified using a radioactive TLCscanner.
-
细胞实验
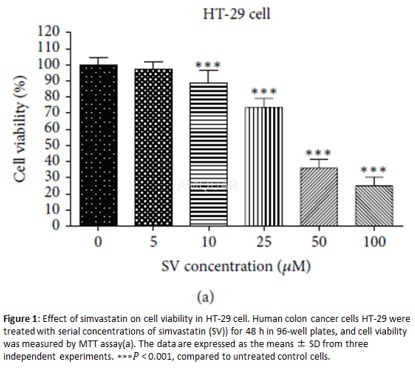
CellCulture[9]
Human HT-29 cells were cultured in DMEMwith 4.5 g/L glucose and 2mM glutamine added with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1.5g/L sodium bicarbonate, 100 ug/mLstreptomycin, and 100 IU/mL penicillin. The medium was exchanged twice a week,and the cells were cultured in 37∘C incubator with 5%CO2. When the cells were confluent (every 5 to 7 days), the cellswere subcultured using trypsin (2.5 g/L) and EDTA (1 g/L). Experiments were carriedout in serum-free medium (SFM) containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin.
MTTAssay
Cell proliferation of HT-29 was measured byMTT assay. The cells were seeded at a density of 5 ×104 cells/mLwith a cultured medium in a 96-well plate. After incubation for 24 h, HT-29cells were treated with various concentration of simvastatin in serum-free mediumfor 24 h. Then MTT (0.5mg/mL) was added to each well and incubated forfurther4h at 37∘C. After the medium has been removed, 100 𝜇L of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)was added to each well by shaking the plate for 10 min. The optical density(OD) was evaluated by DTX 880Multimode Detector at 570 nm. Each assay wasperformed in triplicate.
-
动物实验
Animal study[10]
16 female SPRD rats were purchased when 8weeks of age and a weight ofapproximately 200 g. The animals were housedtogether in groups of four, in type IV cages containing ordinary bedding, ASTPwooden bricks and a shelter. The laboratory and stable were maintained at aconstant temperature of 22± 1 oC, 60±0% humidity, 12:12 h light: dark regime(lights on at 06:00 h) and food and tap water ad libitum. At 14 weeks of ageand a mean weight of approximately 280 g, the rats were exposed to Simvastatin(SV) for a 14-days period. The rats were randomized into four groups eachcontaining four rats. The control group (CT) received vehicle alone (X-trachocolate spread), the low dose group (L) received 1.3 mg SV/kg bw/day, themiddle dose group (M) received 5.0 mg/kg bw/day and the high dose group (H)received 20.0 mg/kg bw/day. The doses used in the animal study were chosen toresemble and encircle the human maintenance dose of SV (40 mg) administered toa standard 60kg woman. A human equivalent dose (HED) may be calculated as follows: HED(mg/kg) = rat dose(mg/kg) x [Km(rat)/Km(human)], where Km= body weight (kg)/body surface (m2),Km(rat) = 6 kg/m2 and Km(human) = 37 kg/m2.Therefore,animal dose (mg/kg) = (40 mg SV/60 mg bw)/day x (37 kg/m2/6 kg/m2)= 4.1 mg SV/kg bw/day. The rats were dosed by mixing SV with X-tra chocolatespread on a cracker once daily starting at 13:00 h. During dosing, rats were housedindividually in cages equipped with a shelter. The animals were observed, bythe responsible person, while consuming their HED(mg/kg) = rat dose(mg/kg) × [Km(rat)/Km(human)], daily dose, andthey were not removed from the cages until all of the animals had finishedtheir daily dose. The weight of the daily intake of X-tra chocolate spread andbiscuits was approximately 0.45g. The weight, mobility, fur and eating anddrinking habits were monitored regularly to ensure the health of the animalsduring the experimental period. On day 15 (24 h after last dose) the rats wereweighed and after-wards euthanized by decapitation in a guillotine. The ratswere euthanized according to the dosing scheme. Total blood volumes (5–10 mL)were immediately collected in heparin-coated Sarstedt tubes. The brain, adrenalglands and ovaries were sampled and frozen in -80◦C until further analysis. All the blood samples were kept cold andcentrifuged (5 min, 4oC, and 5000rpm) to separate plasmafrom the red blood cells. The plasma samples were collected and stored at −80◦C until further analysis. Due tovariations in steroid hormone production during the estrous cycle, the ratswere allowed to synchronize their cycles, by housing the rats together for 40days prior to initialization of the experiment, and the rats were killed inproestrous. The estrous phase was confirmed in individual rats by microscopicinvestigation of vaginal smears.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Dansette PM, Jaoen M, Pons C. HMG-CoA reductase activity in human liver microsomes: comparative inhibition by statins. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology. 2000;52(2):145-148.
[2] Kurakata S KM, Shimada Y, Komai T, Nomoto K. Effects of different inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, pravastatin sodium and simvastatin, on sterol synthesis and immunological functions in human lymphocytes in vitro. Immunopharmacology. . 1996;34(1):51-61.
[3] Masters BA PM, Flint OP, Gregg RE, Wang-Iverson D, Durham SK. In vitro myotoxicity of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors, pravastatin, lovastatin, and simvastatin, using neonatal rat skeletal myocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1995 131(1):163-174.
[more]
分子式
C25H38O5 |
分子量
418.57 |
CAS号
79902-63-9 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
>25 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
>25 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT02061397 | Lymphangioleiomyomatosis|Tuberous Sclerosis Complex | Drug: Simvastatin | University of Pennsylvania|The LAM Foundation | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2014-03-01 | 2016-09-01 |
| NCT03011931 | Celiac Disease | Drug: Simvastatin | Mayo Clinic | | 2016-03-01 | 2017-01-03 |
| NCT01073007 | Stroke, Acute | Drug: Simvastatin | Hospital Universitari Vall d'Hebron Research Institute | Phase 4 | 2009-04-01 | 2016-12-20 |
| NCT01702246 | Sickle Cell Disease | Drug: Simvastatin | Children's Hospital & Research Center Oakland|University of California, Los Angeles | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2012-02-01 | 2016-10-26 |
| NCT00246701 | Hypertriglyceridemia | Drug: Simvastatin + Lovaza|Drug: Simvastatin | GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 3 | 2005-11-01 | 2009-12-10 |
| NCT01147692 | Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 | Biological: simvastatin plus albiglutide | GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 1 | 2010-05-01 | 2016-11-30 |
| NCT01160978 | Heart Failure|Respiratory Failure|Liver Failure|Kidney Failure|Transplantation | Drug: Simvastatin|Drug: Placebo | Helsinki University Central Hospital|Helsinki University|Academy of Finland | Early Phase 1 | 2010-06-01 | 2014-06-19 |
| NCT01561482 | Prostate Carcinoma | Drug: Metformin|Drug: Simvastatin | Nicholas Mitsiades|Baylor College of Medicine | Phase 2 | 2012-01-01 | 2015-07-20 |
| NCT02433535 | Severe Asthma | Drug: Simvastatin | Amir A. Zeki, MD|University of California, Davis | Phase 2 | 2015-05-01 | 2015-05-04 |
| NCT01266434 | Asthma | Drug: Simvastatin|Drug: B1-6-12 | Mahidol University | Phase 3 | 2011-01-01 | 2016-03-15 |
| NCT00819403 | Metabolic Syndrome | Drug: simvastatin|Drug: ezetimibe/simvastatin | University of Maryland|Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Phase 4 | 2009-01-01 | 2014-12-10 |
| NCT00769210 | Heart Failure | Drug: Simvastatin | University of Utah | Early Phase 1 | 2005-05-01 | 2016-03-29 |
| NCT00935259 | Hypercholesterolemia, Dyslipidemia | Drug: Simvastatin|Drug: Placebo | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Phase 1 | 2009-07-01 | 2015-10-07 |
| NCT00334542 | Breast Cancer | Drug: simvastatin | Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center|National Cancer Institute (NCI) | Phase 2 | 2006-03-01 | 2013-07-03 |
| NCT02161822 | Adenocarcinoma of Rectum | Drug: simvastatin | Samsung Medical Center | Phase 2 | 2014-10-01 | 2017-02-15 |
| NCT00508027 | Sickle Cell Disease | Drug: Simvastatin | Children's Hospital & Research Center Oakland|Department of Health and Human Services|FDA Office of Orphan Products Development | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2007-06-01 | 2013-08-20 |
| NCT01167933 | Healthy | Drug: Simvastatin | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2005-01-01 | 2010-08-05 |
| NCT01167894 | Healthy | Drug: Simvastatin | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2005-01-01 | 2010-07-21 |
| NCT00487461 | Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage|Cerebral Vasospasm | Drug: Simvastatin 40 mg|Drug: Placebo|Drug: Simvastatin 80 mg | University of Illinois at Chicago | | 2007-05-01 | 2015-10-22 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们