-
生物活性
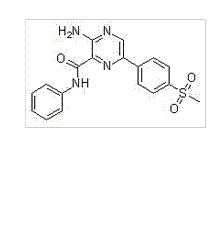
VE-821 is a potent and selective ATP competitive inhibitor of ATR with Ki/IC50 of 13 nM/26 nM which shows excellent selectivity for ATR with minimal cross-reactivity against the related PIKKs ATM, DNA-PK, mTOR and PI3K (Kis of 16 μM, 2.2 μM, >1 μM and 3.9 μM, respectively. VE-821 alone commits a large fraction of cancer cell populations to death, but it only reversibly limits cell cycle progression in normal cells, with minimal death or long-term detrimental effects. Inhibits H2AX cell growth with IC50 of 800 nM. VE-821 is the first highly selectiveand potent ATP-competitive inhibitor of ATR and shows asignificant radio- and chemo-sensitizing effect delimited to cancer cells(largely p53-deficient) without affecting normal cells.
Kinaseactivities of VE-821
Impairmentof CHEK1 phosphorylation by VE-821[3]
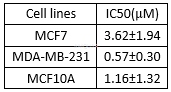
In vitro activities of VE-821
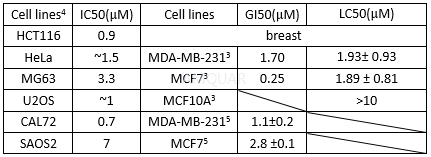
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol
-
激酶实验
Kinase Inhibition Assays[2]
The ability of compounds to inhibit ATR, ATMor DNAPK kinase activity was tested using a radiometricphosphate incorporationassay, as described in Table 5 and below. A stock solution was preparedconsisting of the appropriate buffer, kinase, and target peptide. To this wasadded the compound of interest, at varying concentrations in DMSO to a finalDMSO concentration of 7%. Assays were initiated by addition of an appropriate [γ-33P]ATP solution and incubated at 25oC. Assays were stopped, after thedesired time course, by addition of phosphoric acid and ATP to a finalconcentration of 100mM and 0.66μM, respectively. Peptides were captured on a phosphocellulosemembrane, prepared as per manufacturer's instructions, and washed six timeswith 200μL of 100mM phosphoric acid, prior to the addition of 100μL ofscintillation cocktail and scintillation counting on a 1450 Microbeta LiquidScintillation Counter. Dose-response data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software.

-
细胞实验
CellCulture[4]
U2OS, HeLa, and CAL72 cells were maintainedin DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS, 2mM l-glutamine, 1% antibiotics. For CAL72,1X ITS liquid media supplement was added to this medium. HCT116, SAOS2 and MG63cell lines studied were cultured in 90% McCoy’s 5A supplemented with10% FCS,2mM l-glutamine, and 1% antibiotics (HCT116), in85% McCoy’s 5A supplementedwith 20% FCS (SAOS2) or in DMEM/Ham’s F12 medium supplemented with 5% FCS, 2mM l-glutamine,and 1% antibiotics (MG63). The U2OS cell line for inducible expression of ATRX(referred to here as U2OSATRX-2) was cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10%doxycycline-free FCS, 2mM l-glutamine, 1% antibiotics, 0.5μg/ml puromycin, 0.7μg/mlG418.
CellViability Assays
For cell viability assays, cells wereseeded in triplicate in 96-well plates and incubated overnight. Different cellnumbers were seeded to determine the cell number needed to obtain 70–90% confluencyof the control sample after 6 days. Optimal starting cell numbers for U2OS,HeLa, HCT116, and MG63 were 500 cells, and for CAL72 and SAOS2 1500 cells. Thefollowing day cells were either treated with DMSO (control) or with increasing concentrations(0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16μM) of the ATR inhibitor VE-821 dissolved in DMSO.Cells were incubated for 6 days without medium change and cell viability wasanalyzed using Cell Titer Glo and a TECAN Infinite M200 plate reader accordingto the manufacturers’ instructions.

-
动物实验
Xenografts[6]
MF1 athymic, nude mice weighing 20 to 30 g wereinoculated subcutaneously with 1 x107 COLO205 cells in 100 mL of aserum-free media and Matrigel mixture (1:1). When the tumors reached about250mm3, the mice were randomized in groups of 8 animals. VE-821 (60mg/kg in a solution in 10% Vitamin E Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol Succinate)was administered by oral gavage on days 0, 1, and 2 of each 4-day cycle. Thecontrol group was treated with vehicle (10% VitE TPGS in water) on days 0, 1,and 2 of each 4-day cycle. A total of 4 treatment cycles were given. Tumorswere measured twice a week by caliper, and volumes were calculated using theformula (lengthxwidth2)/2. Body weight was assessed twice a week.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Reaper PM, Griffiths MR, Long JM, et al. Selective killing of ATM- or p53-deficient cancer cells through inhibition of ATR. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7(7):428-430.
[2] Charrier JD, Durrant SJ, Golec JM, et al. Discovery of potent and selective inhibitors of ataxia telangiectasia mutated and Rad3 related (ATR) protein kinase as potential anticancer agents. J Med Chem. 2011;54(7):2320-2330.
[3] Abdel-Fatah TM, Middleton FK, Arora A, et al. Untangling the ATR-CHEK1 network for prognostication, prediction and therapeutic target validation in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2015;9(3):569-585.
[more]
分子式
C18H16N4O3S |
分子量
368.41 |
CAS号
1232410-49-9 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
68 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
约30 mg/mL
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们