| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
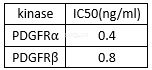
| NCT01393912 | Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma|Progressive or Refractory High-Grade Glioma | Drug: Crenolanib | St. Jude Children's Research Hospital|Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc.|The V Foundation for Cancer Research | Phase 1 | 2011-07-01 | 2016-10-31 |
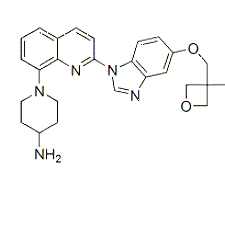
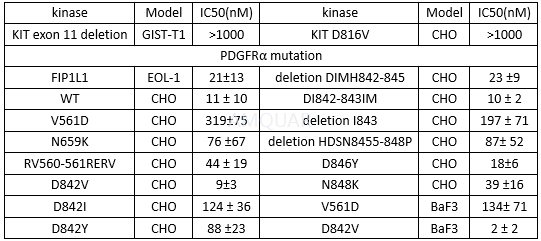
| NCT02847429 | GIST With D842V Mutated PDGFRA Gene | Drug: Crenolanib|Drug: Placebo | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc.|Centre Leon Berard|Fox Chase Cancer Center | Phase 3 | 2016-08-01 | 2017-03-15 |
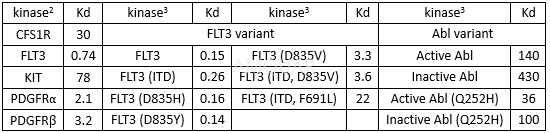
| NCT01522469 | Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia With FLT3 Activating Mutations | Drug: Crenolanib Besylate (CP-868,596-26) | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2012-07-01 | 2015-03-18 |
| NCT01657682 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia With FLT3 Activating Mutations That Has Relapsed or Been Refractory After One or More Prior Therapies | Drug: Crenolanib besylate | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2012-10-01 | 2017-01-26 |
| NCT02626364 | Recurrent/Refractory Glioblastoma | Drug: crenolanib | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2016-04-01 | 2016-07-27 |
| NCT01243346 | D842-related Mutant GIST | Drug: Crenolanib besylate (CP-868,596-26), Dose: 140mg BID | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2011-04-01 | 2014-11-04 |
| NCT02400255 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Drug: Crenolanib besylate | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2015-09-01 | 2016-07-21 |
| NCT02400281 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Drug: Crenolanib besylate|Drug: Idarubicin|Drug: Cytarabine|Drug: Azacytidine|Drug: Mitoxantrone|Drug: Etoposide|Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: G-CSF | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2015-09-01 | 2016-07-21 |
| NCT01229644 | Glioma | Drug: Crenolanib (CP-868,596) | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2011-04-01 | 2012-11-26 |
| NCT02283177 | Newly Diagnosed AML With FLT3 Activating Mutations | Drug: crenolanib|Drug: cytarabine|Drug: daunorubicin|Drug: idarubicin | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2015-01-01 | 2016-10-10 |
| NCT02270788 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Drug: Crenolanib|Drug: Sorafenib|Drug: methotrexate, hydrocortisone and cytarabine with leucovorin | St. Jude Children's Research Hospital|Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc.|Ohio State University | Phase 1 | 2014-10-01 | 2016-11-03 |
| NCT02298166 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Drug: chemotherapy (Mitoxantrone, Cytarabine)|Drug: Placebo|Drug: Crenolanib|Other: Allogeneic stem cell transplantation | University of Ulm | Phase 3 | 2016-11-17 | 2017-03-15 |
| NCT02626338 | Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | Drug: Crenolanib|Drug: Mitoxantrone|Drug: Cytarabine|Drug: Etoposide|Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: G-CSF|Drug: Idarubicin | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2016-02-01 | 2017-01-23 |
| NCT02829840 | Leukemia|FLT3-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia|FLT3-Mutated High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome | Drug: Ponatinib|Drug: 5-azacytidine|Behavioral: Phone Calls | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|Ariad Pharmaceuticals | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2016-09-01 | 2016-08-05 |
| NCT00949624 | Advanced Solid Tumors | Drug: CP-868,596|Drug: Docetaxel|Drug: CP-868,596|Drug: Docetaxel|Drug: CP-868,596|Drug: Docetaxel|Drug: CP-868,596|Drug: AG-013736|Drug: Docetaxel | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 1 | 2005-12-01 | 2012-01-18 |
| NCT00386555 | Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung | Drug: docetaxel|Drug: CP-868,596 + docetaxel|Drug: AG-013736 + docetaxel|Drug: CP-868,596 + AG-013736 + docetaxel | Arog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2007-05-01 | 2012-08-07 |