-
生物活性
E64d (Aloxistatin)is a membrane-permeable prodrug ethyl ester of its biologically active acidform E64c that irreversibly and selectively inhibits cysteine proteases(papain, calpains, and cathepsins) by forming a thioether with the active-sitecysteine. Inhibitor of cathepsins B and L; also thought to inhibit calpain. Inhibits lysosomal proteases and interferes with autolysosomal digestion when used in combination with pepstatin A. Lysosome and cell permeable.
Enzymeactivities of E64c, the active acid form of E64d[1]
E64dinhibits replication of MHV with an ID50 of less than 50μg/ml.[2]
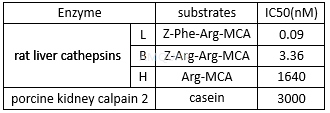
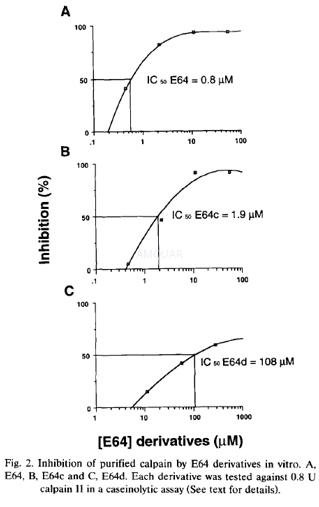
E64dinhibits purified calpain II with an IC50 of 108μM.[3]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
Calpain enzyme activity assays wereperformed using FITC-labeled casein as substrate in a 30 min assay at 30°C. 1unit of calpain was defined as that amount of calpain which released 1μgFITC-casein fragments/min. Inhibition of calpain activity by E64 derivativeswas measured in the presence of 0.8 U of calpain II purified from porcineheart.[3]
-
细胞实验
CellCulture[4]
MC3T3-E1 mouse osteoblastic cells wereroutinely maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2 in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's media (DMEM) containing 10% newborn calf serum(NCS), 2mmol/L glutamine, penicillin (100U/mL), and streptomycin (100μg/mL).
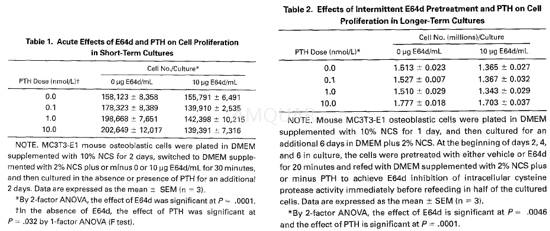
AcuteEffects of E64d and PTH on Cell Proliferation in Short-Term Cultures
MC3T3-E 1 cells were plated at a density of3.5 × 103/cm 2, cultured under routine conditions for2days, and switched to DMEM supplemented with 2% NCS plus vehicle or E64d (10μg/mL)for 30minutes. The pretreatment media were then removed and replaced with DMEM supplementedwith 2% NCS and 0.0, 0.1, 1.0, or 10nmol/L PTH, and the cells were cultured foran additional 2days. The spent media were aspirated, and the cultures wererinsed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The cells were liberated by mildtrypsinization, pelleted by centrifugation at 800 × g for 15minutes at 22°C,and resuspended in 2.0mL of PBS. The cell number was determined in triplicate250-pL aliquots of cell suspension diluted in 20mL Isoton using a Z1 Coulter connter.
Effectsof Intermittent E64d Pretreatment and Short-Term PTH Administration on Cell Proliferationin Longer-Term Cultures
The cells were plated and cultured for24hours in DMEM containing 10% NCS. The cells were then cultured for anadditional 6 days, during which time they were subjected to three 2-day cyclesof pretreatment with vehicle or E64d (10μg/mL) for20minutes, followed by refeeding with DMEM supplemented with 2% NCS plus 0.0,0.1, 1.0, or 10.0nmol/L PTH. Cells were harvested and counted as alreadyoutlined.
-
动物实验
ExperimentalAnimals[5]
Sixty-nine adult male Sprague-Dawley ratsweighing between280 and 340 g were divided randomly into three groups: sham,DMSO, and E64d.
TransientMiddle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
Rats were weighted prior to surgery.Anesthesia was induced with ketamine (80 mg/kg i.p.), followed by atropine (0.1mg/kg). A heating pad and a heating lamp were used to maintain the rectaltemperature between 36.5oC ±0.5oC.Rats were intubated and respiration was maintained with a small animalrespirator. Rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO),with some modifications. Briefly, with the use of an operating microscope, theleft common carotid artery, internal carotid artery (ICA), and external carotidartery (ECA) were surgically exposed. The ECA was then isolated and coagulated.A 4-0 silicon-coated nylon suture was inserted into the ICA through the ECAstump and gently advanced to occlude the MCA. The mean arterial blood pressure,heart rate, arterial blood gases, and blood glucose levels before, during, andafter ischemia were analyzed. After 2hr of MCA occlusion, the suture wasremoved to restore blood flow, the neck incision was closed, and the rats wereallowed to recover. After the experiment, the animals were housed individuallyuntil sacrifice. All animals had free access to food and water.
TreatmentMethods
The treatment group was injected with E64d (5mg/kgi.p) 30 min before focal ischemia. E64d was diluted with 1% dimethyl sulfoxide(DMSO) to a concentration of 15 mg/ml. In the DMSO group, the rats were treatedwith the same volume of DMSO that was delivered i.p. 30 min before focalischemia.
NeurologicalScore
The neurological scores were evaluated 24hrafter MCAO by using the scoring system.
2,3, 5-Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride Staining and Evaluation of Infarction Volume
Samples from sham (n= 3), MCAO (n = 6), andE64d (n = 6) groups were used for evaluation of infarction volume. Twenty-fourhours after MCAO, rats were deeply anesthetized with ketamine and perfusedtranscardially with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Then, rats weredecapitated, after which the brains were rapidly removed. All brains werecarefully evaluated for macroscopic hemorrhagic changes before2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining. The tissue was sliced into2-mm-thick coronal sections, and the slices were stained in TTC for 30 min at37oC in the dark. When the stain had developed, the tissue blockswere moved into 10% formalin overnight. Seven coronal sections per animal werethen photographed. TTC stains both neuronal and glial cells with a deep redpigment. In areas where neuronal loss occurs, TTC does not stain and tissueremains white. Hence, the areas of unstained tissue (the infarcted areas) weredemarcated and were analyzed in Image J (NIH) version 1.32.
NisslStaining
Samples from sham (n =2), MCAO (n= 4), andE64d (n= 4) groups were used for histological assessment. Twentyfour hoursafter the MCAO, rats were anesthetized and transcardially perfused withice-cold PBS followed by 10% paraformaldehyde paraformaldehyde. Thebrains were quickly removed and postfixed in 10% paraformaldehyde and 30%sucrose for 3 days. The brains were cryoprotected and then rapidly frozen by2-meyhtlbutane chilled in liquid nitrogen. Coronal tissue sections 10 lm thickwas cut with the aid of a cryostat.
For Nissl staining, slices were hydrated in0.1% cresyl violet for 3 min. Then they were dehydrated in ethanol and cleanedwith xylenes. The slides were next examined via light microscopy, and pictureswere taken with a digital camera.

-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Hook G, Jacobsen JS, Grabstein K, Kindy M, Hook V. Cathepsin B is a New Drug Target for Traumatic Brain Injury Therapeutics: Evidence for E64d as a Promising Lead Drug Candidate. Front Neurol. 2015;6:178.
[2] Kim JC SR, Currier PF, Lu X, Denison MR. Coronavirus protein processing and RNA synthesis is inhibited by the cysteine proteinase inhibitor E64d. Virology. 1995 208(1):1-8.
[more]
分子式
C17H30N2O5 |
分子量
342.43 |
CAS号
88321-09-9 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
52 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
50 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们





















