-
生物活性
Pazopanib is a potent and selective multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) and c-kit, which are key proteins responsible for tumor growth and angiogenesis.
Pazopanibinhibits VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 in HUVEC cells with an IC50 of∼8 nM.[1]
Kinase selectivity of pazopanib

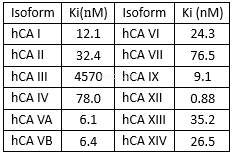
Theactivities of pazopanib against the carbonic anhydrases (CAs)[3]
Inhibitionof Cellular Proliferation

-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
Kinase Enzyme Assays[1]
VEGFR enzyme assays for VEGGR1, VEGFR2, andVEGFR3 were run in homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) format in 384-wellmicrotiter plates using a purified, baculovirus-expressedglutathione-S-transferase (GST) fusion protein encoding the catalyticc-terminus of human VEGFR receptor kinases 1, 2, or 3. Reactions were initiatedby the addition
of 10μL of activated VEGFR2 kinase solution[final concentration, 1nM enzyme in 0.1M4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), pH 7.5, containing0.1 mg/mL bovine serum albumin (BSA), 300μM dithiothreitol (DTT)] to 10μLsubstrate solution [final concentration, 360 nM peptide,(biotin-aminohexyl-EEEEYFELVAKKKK-NH2), 75μM ATP, 10μM MgCl2], and 1μLof titrated compound in DMSO. Plates were incubated at room temperature for 60min, and then the reaction was quenched by the addition of 20μL of 100mMethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA). After quenching, a 20μL HTRF reagent(final concentration, 15nM Streptavidin-linked allophycocyanin, 1nMEuropium-labeled antiphosphotyrosine antibody diluted in 0.1mg/mL BSA, 0.1 MHEPES, pH 7.5) was added and the plates incubated for a minimum of 10 min. The fluorescenceat 665nM was measured with a Wallac Victor plate reader using a time delay of50μs.
-
细胞实验
CellCulture and Reagents[6]
Human bladder cancer cells HTB3, HT1376,J82, RT4, CRL1749, T24, Sup, and HTB9 were grown in Opti-MEM with 3.75% fetalbovine serum and 100 μ/mL streptomycin-penicillin sulfate. All cell lines were incubatedat 37°C with 5% CO2. Pazopanib was dissolved in dimethyl sufloxide(DMSO).
CellViability Assay
For all experiments, the cell viability wasassessed using a tetrazolium-based assay. Approximately 3000 cells in 50μLof media per well were plated in 96-well plates in triplicate. Twenty-fourhours after plating, the cells were subjected to specific treatment regimenswith the addition of 50Μl of treatment media to achieve the prescribed treatmentconcentrations. DMSO, in equal amounts to the treatment conditions, was addedto the media in the control condition. Once the treatment was complete, 20μLof the AQueous 1 solution was added to each well, for a final volume of 120μL.Colorimetric analysis using a 96-well plate reader was performed between 1 and4 hours (wavelength of 490 nm) after the addition of AQueous 1 solution,depending on cell type and cell density. Cell viability assays were performedin triplicate. Synergy analysis was performed with the CalcuSyn software program(version 2-2005) using nonconstant ratio analysis and statistical method tocalculate the combination index (CI) values. The resulting CI is a quantitativemeasurement of the degree of interaction between difference drugs. A CI valueof 1 signifies an additive effect, a CI more than 1 denotes antagonism, and aCI of less than 1 indicates synergy.

-
动物实验
Xenograftmouse model and treatment[7]
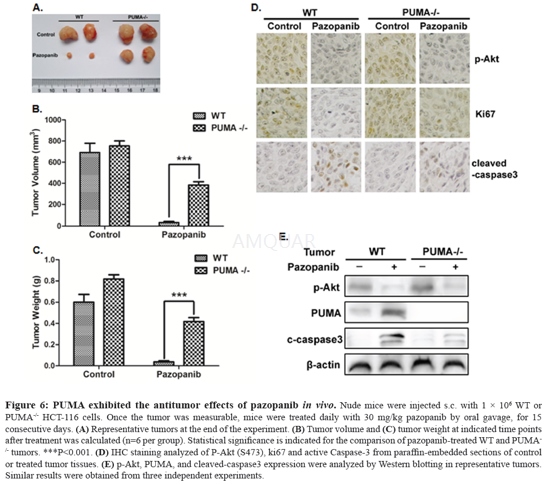
WT and PUMA-/- HCT-116 xenografts were establishedand measured. Female 5- to 6-week-old nude mice were housed in a sterileenvironment with micro isolator cages and allowed access to water and chow adlibitum. 1 × 106 cells were resuspended in 100μl of PBS(phosphate-buffered saline solution) and injected subcutaneously into theflanks of nude mice. Once the tumor was measurable, mice were given daily 30mg/kg pazopanib or vehicle control by oral gavage. Pazopanib was resuspended in0.5% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and 0.1% Tween-80 in water as avehicle (pH 1.3-1.5) before use. Mice were treated for 7 daysa week, andterminated after 15 days treatment. Tumor growth was monitored by calipers, andtumor volumes were calculated according to the formula 0.5 × length × width2.Mice were euthanized when tumors reached ~1.0cm3 in size.
Autopsyand histopathology
Animals were autopsied when the tumorreached to the maximal size and tissues were collected and examined.Experimental and control tissue samples were fixed in 10% neutral-bufferedformalin 24 hours, and washed once with 1X PBS and then transferred into 70% ethanoland stored at 4°C. Tissues were proceed by ethanol dehydration and embedded inparaffin by Lecia according to standard protocols. Sections (5μm) were preparedfor immunohistochemisty. In breif, after antigen retrieval with citric acid (pH6.0) endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked with 1% hydrogen peroxide.Primary antibody (anti-P-Akt (Ser473), Ki67 and c-caspase3 antibody, dilution1:200) was applied and incubated with secondary anti-bodies conjugated toperoxidase labeled dextran polymer. Sections not exposed to secondary antibodyserved as negative controls.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Harris PA BA, Cheung M, Kumar R, Crosby RM, Davis-Ward RG, Epperly AH, Hinkle KW, Hunter RN 3rd, Johnson JH, Knick VB, Laudeman CP, Luttrell DK, Mook RA, Nolte RT, Rudolph SK, Szewczyk JR, Truesdale AT, Veal JM, Wang L, Stafford JA. Discovery of 5-[[4-[(2,3-dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)methylamino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-2-methyl-benzenesulfonamide (Pazopanib), a novel and potent vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor. J Med Chem. . 2008;51(15):4632-4640.
[2] Kumar R, Crouthamel MC, Rominger DH, et al. Myelosuppression and kinase selectivity of multikinase angiogenesis inhibitors. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(10):1717-1723.
[3] Winum JY, Maresca A, Carta F, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT. Polypharmacology of sulfonamides: pazopanib, a multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical use, potently inhibits several mammalian carbonic anhydrases. Chem Commun (Camb). 2012;48(66):8177-8179.
[more]
分子式
C21H23N7O2S |
分子量
437.52 |
CAS号
444731-52-6 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
80 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT01361334 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Drug: Pazopanib | University Hospital Muenster|Novartis | Phase 2 | 2011-06-01 | 2017-03-14 |
| NCT01072890 | Solid Tumors | Drug: Temsirolimus, Pazopanib | University of California, Davis|GlaxoSmithKline|Pfizer | Phase 1 | 2010-02-01 | 2012-03-26 |
| NCT01521715 | Locally Advanced and/or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma|Carcinoma, Renal Cell|Clear-cell Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma | Drug: Pazopanib | iOMEDICO AG|Novartis Pharmaceuticals | Phase 4 | 2011-12-01 | 2016-06-01 |
| NCT01642017 | Metastatic Cancer (Different Solid Tumour Types) | Drug: Pazopanib | Institut Claudius Regaud|GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 1 | 2015-03-01 | 2015-03-26 |
| NCT01430572 | Advanced Cancers|Solid Tumors | Drug: Pazopanib|Drug: Everolimus | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|GlaxoSmithKline|National Comprehensive Cancer Network | Phase 1 | 2011-10-01 | 2017-02-08 |
| NCT01600573 | Ovarian Cancer | Drug: pazopanib in combination with weekly topotecan | JSehouli|GlaxoSmithKline|Charite University, Berlin, Germany | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2012-05-01 | 2016-10-10 |
| NCT02795819 | Renal Cell Carcinoma|Soft Tissue Sarcoma|Metastatic Disease | Drug: AR-42|Drug: Pazopanib | Virginia Commonwealth University|Arno Therapeutics|National Cancer Institute (NCI) | Phase 1 | 2016-07-08 | 2017-03-03 |
| NCT01253369 | Small Cell Lung Cancer|Lung Cancer|SCLC | Drug: Pazopanib | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute|Massachusetts General Hospital|Brigham and Women's Hospital|Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center|GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 2 | 2010-06-01 | 2015-12-08 |
| NCT01545817 | Carcinoma, Renal Cell | Drug: Pazopanib followed by everolimus | Novartis | Phase 2 | 2012-04-01 | 2017-01-11 |
| NCT01392352 | Renal Cell Carcinoma|Soft Tissue Sarcoma|Glioblastoma|Ovarian Cancer|Cervical Cancer|Breast Cancer|Non-small Cell Lung Cancer|Small Cell Lung Cancer|Pancreatic Cancer|Melanoma|Gastrointestinal Cancer | Drug: Pazopanib | Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust|University of Cambridge|GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 2 | 2011-04-01 | 2016-01-04 |
| NCT01975519 | Advanced Soft Tissue Sarcoma | Drug: TRC105 and Pazopanib | Tracon Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2013-12-01 | 2017-02-21 |
| NCT01130805 | Gastric Cancer | Drug: Pazopanib in combination with capecitabine and oxaliplatin | Samsung Medical Center | Phase 2 | 2010-12-01 | 2016-04-13 |
| NCT02324803 | Self Efficacy|Adverse Drug Event|Carcinoma, Renal Cell | Drug: pazopanib | Southern China Urology Cancer Consortium | Phase 2 | 2014-07-01 | 2014-12-18 |
| NCT01107665 | Stage III Melanoma|Stage IV Melanoma|Unresectable Melanoma | Drug: Pazopanib and Paclitaxel | University of California, Irvine|GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 2 | 2010-08-01 | 2016-12-06 |
| NCT02138526 | Cancer | Drug: pazopanib|Other: continental breakfast | Radboud University | Phase 1 | 2014-06-01 | 2016-09-15 |
| NCT01257750 | Corneal Neovascularization | Drug: Pazopanib (5mg/ml) | Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2010-11-01 | 2012-10-05 |
| NCT01339871 | Advanced Cancer | Drug: Pazopanib|Drug: Vorinostat | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | Phase 1 | 2011-04-01 | 2016-12-27 |
| NCT01743482 | Germ Cell Tumors|Measurable Disease|Relapse or Progression After 2 or 3 Chemotherapy Regimens.|Relapse or Progression After High-dose Chemotherapy. | Drug: Pazopanib | Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milano|GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 2 | 2013-01-01 | 2012-12-04 |
| NCT01330966 | Chondrosarcoma|Metastatic Chondrosarcoma | Drug: pazopanib | Vector Oncology|GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 2 | 2011-04-01 | 2017-01-16 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们






















