-
生物活性
Tubastatin A HCl is a potent HDAC6 inhibitor with IC50 of 15 nM.
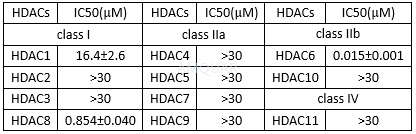
EnzymeInhibition for Tubastatin A[1]
TubastatinA inhibits TNF-α and IL-6 production from LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells with anIC50 of 272.5 nM and 712.9 nM respectively.[2]
TubastatinA inhibits nitric oxide (NO) secretion in murine Raw 264.7 macrophages with anIC50 of 4.2 μM.[2]
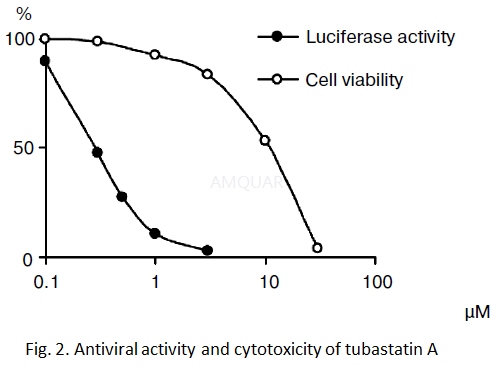
TubastatinA suppressed the HCV replicon with EC50 of 0.3 μM.[3]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80
-
激酶实验
EnzymeInhibition Assay Methods[1]
Enzyme inhibition assays were performed bythe Reaction Biology Corporation, Malvern, PA, using the Reaction Biology HDACSpectrum platform. The HDAC1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 assays usedisolated recombinant human protein; HDAC3/NcoR2 complex was used for the HDAC3assay. Substrate for HDAC1, 2, 3, 6, 10, and 11 assays is a fluorogenic peptidefrom p53 residues 379-382 (RHKKAc); substrate for HDAC8 is fluorogenic diacylpeptide based on residues 379-382 of p53 (RHKAcKAc). Acetyl-Lys(trifluoroacetyl)-AMC substrate wasused for HDAC4, 5, 7, and 9 assays. Compounds were dissolved in DMSO and testedin 10-dose IC50 mode with 3-fold serial dilution starting at 30 μM. ControlCompound Trichostatin A (TSA) was tested in a 10-dose IC50 with 3-fold serialdilution starting at 5 μM. IC50 values were extracted by curve-fitting the dose/response slopes.
-
细胞实验
Cellcultures
Cell lines HepG2 and Huh7 were grown inmedium DMEM + F12 (2 : 1) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mlpenicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin in the presence of 5% CO2 at37°C. The cells were seeded once per three days at the ratio of 1 : 3 or 1 : 5.The line Huh7- luc/neo culture was grown under the same conditions on additionof G418 (330 μg/ml).
Inhibitionof HDAC6 in hepatocytes
Cells were seeded into a 6-well cultureplate. 24 hours later (the monolayer was 40-50%) compounds under test wereintroduced into the culture medium and the cultures were incubated at 37°C inthe presence of 5% CO2. Three days later (the monolayer in thecontrol sample was 100%) the medium was removed, and the cells were washed withPBS and treated with a lysing reagent.
Antiviralactivity
The Huh7-luc/neo cells were seeded into a48-well culture plate (the medium did not contain antibiotic G418). After 24 h(the monolayer was 40-50%) the culture medium was supplemented with compounds undertesting in different concentrations and incubated at 37°C in the presence of 5%CO2. Three days later (the monolayer in the control sample was 100%)the medium was removed, the cells were washed with PBS and lysed, and theluciferase activity of the reporter protein was measured using a LuciferaseAssay System Kit according to the producer’s protocol. Chemiluminescence wasmeasured with a Thermo Luminometer.
Cytotoxicity
The Huh7 cells were seeded into a 96- wellculture plate the day previous to addition of the compounds under test. After24 h (the monolayer was40-50%) the culture medium was added with the compounds undertest in different concentrations and incubated at 37°C in the presence of 5%CO2. Three days later (the monolayer in the control sample was 100%) the cellviability was determined with an MTT Kit according to the producer’s protocol.
-
动物实验
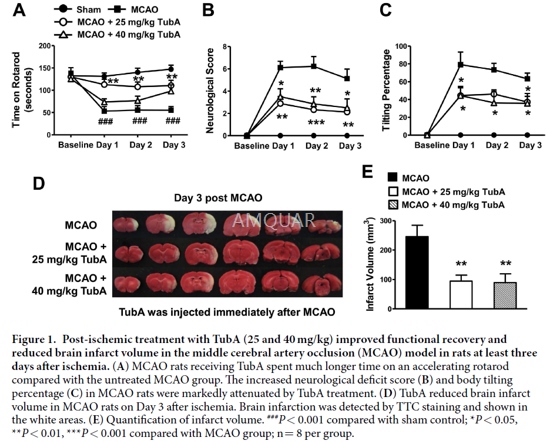
MCAOand drug administration
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200–220 g) underwentright middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) under inhalational anesthesia(2.5% isoflurane in O2). Tubastatin A (TubA) was first dissolved indimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted with 2% Tween20 in phosphate bufferedsaline (PBS). The final concentration of DMSO was 5%. MCAO rats were randomizedto TubA or vehicle treatment. TubA (25 or 40 mg/kg, i.p.) was injectedimmediately or 24 hours after ischemic onset, and then once daily for up tothree days.
Behavioraltests
The accelerating rotarod test, neurologicaldeficit score, and elevated body tilting test were performed for threeconsecutive days after ischemia to assess the effects of TubA on the functionalrecovery of MCAO rats by an investigator blind to the treatment condition.Briefly, for the accelerating rotarod test, rats were placed on an acceleratingrotarod apparatus, in which the speed was accelerated from 0 to 40 rpm overfour minutes. Three consecutive days before MCAO, rats received once-dailytraining sessions of three trials separated by 30-minute intervals. The longestamount of time each rat remained on the rod was recorded as baseline. Threeconsecutive days after MCAO, rats underwent three trials on the rotarod, andthe best performance of each rat was recorded for that day.
For the neurological deficit score, ratswere assessed for motor, sensory, and reflex performance using a modified 12-pointneurological scoring system. Seven tests of motor performance (flexion offorelimb, flexion of hind limb, head movement 10° to the vertical axis,inability to walk straight, circling towards the paralytic side, falling to theparalytic side, and immobility), two tests of sensation (visual and tactileplacement and a proprioceptive test), and three reflex tests (pinna, corneal,and startle reflex) were evaluated. A score of 0 (normal) or 1 (abnormal) wasgiven for each test.
Body asymmetry was quantitatively assessedusing the elevated body tilting test. Rats were examined for lateralmovements/turning when their bodies were suspended by the tail 200 mm above thetesting table. The number of initial head or upper body turns was counted in 20consecutive trials.
Braininfarction measurement
Rats were sacrificed immediately afterbehavioral tests on Day 3 after ischemia, and the brains were quickly removedand placed on ice. TTC (2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride) staining wasperformed to determine brain infarct volume. Briefly, six 2-mm coronal sectionswere stained with 2% TTC at 37 °C for 15 minutes and then fixed in 10% formalinovernight. The infarct area in white was measured using ImageJ software. Theinfarct volume was calculated as the sum of infarct area times the averageslice thickness (2 mm).
Immunofluorescencestaining
Brains were fixed with 10% formaldehyde bytranscardial perfusion, dehydrated in 30% sucrose, and cryo-cut coronally at 30μm. Free-floating sections were incubated with 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5minutes, blocking solution (1% BSA with 0.05% Triton X-100) for 2 hours, andthen overnight at 4 °C with mouse anti-NeuN (1:1,000) in blocking solution.After washing, sections were incubated with Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugatedsecondary antibody (1:2000). Immunolabeling signals were captured by a ZeissAXIO Imager M2 microscope. ImageJ was used to quantify the results.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Butler KV KJ, Brochier C, Vistoli G, Langley B, Kozikowski AP. Rational design and simple chemistry yield a superior, neuroprotective HDAC6 inhibitor, tubastatin A. J Am Chem Soc. . 2010 132(31):10842-10846.
[2] Vishwakarma S, Iyer LR, Muley M, et al. Tubastatin, a selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor shows anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic effects. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;16(1):72-78.
[more]
分子式
C20H22ClN3O2 |
分子量
371.86 |
CAS号
1310693-92-5 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
75 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
30 mg/mL
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们




















