-
生物活性
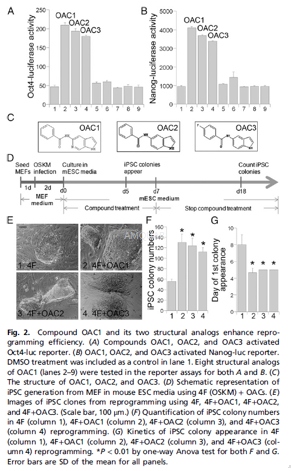
OAC1 is an Oct4 activator which enhances and accelerates iPSC reprogramming in the presence of 4F (Oct4, Sox-2, c-Myc and GKLF) by ~20-fold (relative to 4F by itself). OAC-1 upregulates mRNA expression of Oct4, Sox-2 and Nanog, as well as Tet1. It has shown no effects on the p53-p21 pathway or Wnt-β-catenin signaling.
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
-
细胞实验
iPSC Derivation in iSF1 Media[1]
OG2 MEFs were seeded onto 6-well plates at the density of 3 × 104 cells per well in DMEM with 10% FBS, 0.1 mM NEAA, and 0.1 mM L-glutamine, 24 h before transduction. Freshly prepared viruses of the 4F, Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc, and Klf4, were added to the cells. Two days after viral infection, the transduced OG2 MEFs were split into new six-well plates with irradiated MEF feeders and cultured in iSF1 reprogramming media containing high-glucose DMEM, 10% knockout serum, 0.5% N2, 5 ng/mL b-FGF, 2 mM L-glutamine, 0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 0.1 mM NEAA, and 1,000 U/mL of LIF. This day was defined as day 0. On day 1, 1 μM of each compound (OAC1, OAC2, and OAC3) was added to the 4Ftransduced OG2 MEFs. Treatment was continued for 1 wk. When iPSC colonies emerged, these colonies were picked for expansion on the irradiated MEF feeders in mouse ESC medium.
Luciferase Reporter Assays
The Oct4-luc or Nanog-luc cells were treated with compound OAC1 or its structural analogs at 1μM concentration or at indicated concentrations in triplicates. Other compounds used include 2μMBIO, 2μMBIX (an inhibitor of the G9a histone methyltransferase), 2μM 5’-azacytidine (AzaC), 25μg/mL Vitamin C (Vc), 10nM Am580 (a retinoic acid receptor agonist), 5 μMtranylcypromine, and 0.5mMvalporic acid (VPA). Luciferase reporter assays were performed 24 h after compound treatment or at indicated time points. For Topflash reporter assays, 0.2μg β-catenin–responsive Topflash reporter gene plasmid was introduced into CV1 cells using trasfection. Compounds were added 6 h after transfection. Luciferase activity was measured 48 h after compound treatment using the Glo Luciferase Assay System.
-
动物实验
In vivo transplantation[2]
Transplantation of human cells into NSG mice was done as described previously14, 15. Briefly, 8–10 week old NSG mice were sublethally irradiated (350cGy; 137Cs source, single dose) and transplanted with progeny of 50000 OAC1 or vehicle control treated CB CD34+ cells within 24h after irradiation. Peripheral bloods were collected at various time points by tail-vein bleeding. The blood samples were treated with RBC lysis buffer and then washed in PBS+1% BSA buffer before staining. Peripheral blood collected from untransplanted NSG mouse was used as a negative control. Mice were sacrificed 16 weeks after transplantation. For long-term engraftment assay, 2×106 BM cells from the primary recipient mice were infused into secondary recipient mice. These mice were also sacrificed 16 weeks after transplantation. BM cells were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry as described above.
Limiting dilution analysis
The frequency of human SRCs in uncultured CD34+ cells and the progeny of an equivalent number of CD34+ cells that were ex vivo expanded in the presence of vehicle control or OAC1 were analyzed by limiting dilution assay as reported by others4. Increasing doses of uncultured CD34+ cells (500, 2500, 5000) or the progeny of an equivalent number of CD34+ cells were infused into NSG mice. These mice were sacrificed 12 weeks after transplantation. The HSC frequency was calculated using L-Calc software and plotted using ELDA software
In vivo teratoma formation assay
1×106CD34+cells from vehicle control cultures or cultures containing OAC1 or 1×106 human H9 ES cells were subcutaneously injected into 6-week-old, Athymic nude mice. The resulting teratomas were removed 6 weeks later. Samples from the teratomas were paraffin-embedded and serially sectioned using microtome. To analyze the three germ-layer lineage cells derived from injected H9 ES cells in the teratomas, sectioned slides were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Images were analyzed using an inverted microscope system.

-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Li W, Tian E, Chen ZX, et al. Identification of Oct4-activating compounds that enhance reprogramming efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(51):20853-20858.
more
分子式
C14H11N3O |
分子量
237.26 |
CAS号
300586-90-7 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
58 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
29 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们