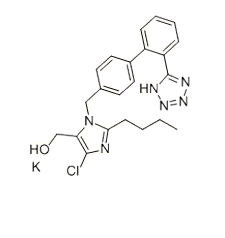
-
生物活性
Losartan Potassium is a selective, non-peptide angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist. Antagonism of the AT1 receptor and interference of association between AT1 and angiotensin II produces vasodilation and reduction of hypertension. This antagonism has other downstream effects, including a correlated antagonism of the thromboxane A2 receptor, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and induction of peroxisome proliferator-actived receptor gamma (PPARγ) activity.
Inhibition of specific binding of [3H] angiotensin II[1]

Binding inhibition of [3H] AII for DuP-753[2]

DuP-753 inhibits the All induced 45Ca+ efflux in rat smooth muscle cells with an IC50 of 20nM.[2]
Losartan inhibits the binding of angiotensin II Angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptors with an IC50 of 20nM.[3]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
Saline
-
激酶实验
Angiotensin II Receptor Binding Assay[1]
Adrenals were obtained after cervical dislocation and kept in ice-cold sucrose buffer containing 0.2 M sucrose, 1 Mm EDTA, and 10mM Tris (pH 7.4). After removal of the medulla, the cortices were minced, rinsed, and homogenized in a chilled ground-glass tissue grinder. The homogenate was spun at 3000g for 10 min, and supernatant was decanted through cheesecloth. Combined supernatants were spun at 12000g for 13min. The final supernatant was then centrifuged at 102000g for 60 min. All of the previous steps were carried out at 4 ℃. The pellet was resuspended in assay buffer containing 0.25% BSA, 5mM MgCl2, and 50mM Tris, pH 7.2 at 25 ℃.
Binding assays were performed by incubating aliquots of freshly prepared particulate fraction (0.02-0.03mg of protein) with [3H]AII (2nM) with or without varying concentrations of inhibitor in 12 x 75mm polystyrene tubes in a final volume of 0.5 mL of assay buffer. After incubation in a shaking incubator for 60 min at 25 ℃, the reaction was terminated by addition of 3 mL of cold assay buffer and the bound and free radioactivity was rapidly passed through glass-fiber filters prewetted with assay buffer. After the filters were air-dried, the trapped radioactivity was determined by scintillation counting. Assays were performed in duplicate. All data presented are specific binding, defined as that displaceable by 1μM unlabeled AII added to the mixture. The inhibitory concentration (IC50) of an inhibitor that gave 50% displacement of the specific binding of labeled AII (2nM) was estimated from the linear portion of the displacement curve. Intraassay and interassay IC50 values for a given test compound may vary between 5-10% and 15-30%, respectively.
-
细胞实验
Cell culture[4]
CHO-AT1 cells were cultivated in 75 cm2flasks in Dulbecco’s Modified Essential Medium (DMEM) which is supplemented with 2mM L-glutamine, 2% of a stock solution containing 5000 I.U./ml penicillin and 5000 mg/ml streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum. The cells are grown in 5% CO2at 37 ℃ until they are confluent.
Inositol phosphate accumulation
The cells were plated in 24 well plates and cultured until almost confluent. The medium was replaced by DMEM containing 10μM unlabeledmyo-inositol and 1μCi/mlmyo-[3H] inositol and the cells were further grown for 20 h in 5% CO2at 37 ℃. Just before the incubation, the cells were washed 2 times with DMEM (0.5 ml per well). DMEM (400 ml) containing 10 mM LiCl was added to each well and the cells were left for 15 min at 37 ℃. Preincubations were initiated by addition of 50μl DMEM/10 mM LiCl either alone (controls) or containing antagonists and proceeded at 37 ℃ for 30 min or the indicated periods of time. Subsequent incubations were started by adding 50μl of DMEM/10 mM LiCl either alone (basal accumulation) or containing angiotensin II and the plates were incubated at 37 ℃ for 5 min or the indicated time periods. Coincubations started by adding 100μl of DMEM/10 mM LiCl either alone (basal accumulation) or containing the antagonists and/or angiotensin II and the plates were incubated at 37 ℃ for 5 min. The denoted inositol phosphate accumulation represents the accumulation of the inositol mono-, bis- and triphosphates. The increase in angiotensin II induced inositol phosphates accumulation was linear between 0 and 10 min and then gradually leveled off. After 30 min the cells still contained approximately 70% of the original incorporated myo-[3H] inositol. Desensitization was only observed at longer incubation times (>15 min).
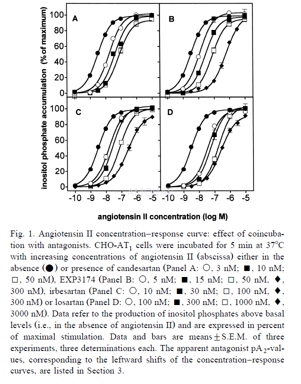
-
动物实验
Animals and drugs[5]
Male albino mices (20-25gm) used in these studies were allowed food and water ad libitum up to the time of experimentation. Prior to use, the mice were housed in polypropylene cages in groups of six to eight animals under natural light-dark cycle.
Losartan potassium, fluoxetine HCl, nortriptyline HCl were dissolved in normal saline and was given i.p. Reserpine was dissolved in a few drops of glacial acetic acid and the volume was makeup with normal saline. The drug solutions were prepared afresh at beginning of each experiment.
In vivo study
In acute studies, all the drugs were administered by i.p. in a constant volume of 1 ml per 100 gm of body weight. In chronic studies, required dose of losartan potassium (3 & 30 mg/kg) was dissolved in per day consumption of drinking water (12mI/100 gm of body weight) and made available for 21 days.
The behavioral despair test has been used as a test of depressive like behavior. 8) The animals were forced to swim individually in glass cylinder (30 cm high, 22.5 cm in diameter) containing 15 cm water at room temperature. The animals were individually trained in 15 min sessions, using the apparatus described above one day prior to the experimentation. During experimentation each animal was placed on the cylinder one at a time and left there for 6 min. The duration of immobility for each mouse was recorded. A mouse was judged to be immobile when it ceased struggling and remaining floating motionless in the water making only movements’ necessary to keep its head above water.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Carini DJ DJ, Aldrich PE, Chiu AT, Johnson AL, Pierce ME, Price WA, Santella JB 3rd, Wells GJ, Wexler RR, et al. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: the discovery of a series of N (biphenylylmethyl)imidazoles as potent, orally active antihypertensives. J Med Chem. . 1991;34(8):2525-2547.
[2] Chiu AT MD, Price WA, Wong PC, Carini DJ, Duncia JV, Wexler RR, Yoo SE, Johnson AL, Timmermans PB. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. VII. Cellular and biochemical pharmacology of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J. Pharmacol. Exper. 1990;252(2):711-718.
more
分子式
C22H23ClKN6O |
分子量
462.01 |
CAS号
124750-99-8 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
93 mg/mL |
Water
90 mg/mL |
Ethanol
98 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
约25 mg/mL
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT03029091 | Eosinophilic Esophagitis | Drug: Losartan Potassium | Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati|National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)|National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)|Office of Rare Diseases (ORD)|National Center for Advancing Translational Science (NCATS) | Phase 2 | 2017-01-19 | 2017-01-20 |
| NCT01989078 | Sickle Cell Disease | Drug: Losartan | Emory University | Early Phase 1 | 2012-12-01 | 2017-02-15 |
| NCT00880386 | Dyspnea|Lung Cancer|Pulmonary Complications|Radiation Fibrosis | Drug: Losartan | University of South Florida|National Cancer Institute (NCI) | | 2009-03-01 | 2013-05-21 |
| NCT00756938 | Hypertension | Drug: losartan potassium | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Phase 3 | 2009-03-01 | 2015-01-14 |
| NCT01149486 | Healthy | Drug: Losartan potassium/Hydrochlorothiazide|Drug: Hyzaar庐 | Teva Pharmaceuticals USA | Phase 1 | 2004-01-01 | 2010-11-22 |
| NCT02238457 | Heart Failure | Drug: Low dose losartan|Drug: High dose losartan | Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute | Phase 4 | null | 2014-09-11 |
| NCT00879879 | Precancerous Condition | Drug: losartan | University of South Florida|National Cancer Institute (NCI) | | 2009-03-01 | 2013-08-09 |
| NCT01324752 | Drug Interaction Potentiation | Drug: PA21 and Losartan with Food|Drug: No PA21; Losartan with food|Drug: PA21 with food and Losartan 2 hours later | Vifor Inc. | Phase 1 | 2011-03-01 | 2012-12-19 |
| NCT01216878 | Hypertension | Drug: losartan potassium | Roxane Laboratories | | 2004-09-01 | 2010-10-06 |
| NCT01216852 | Hypertension | Drug: Losartan Potassium | Roxane Laboratories | | 2004-08-01 | 2010-10-06 |
| NCT02769130 | Pulmonary Vein Stenosis|Children | Drug: Losartan | The Hospital for Sick Children | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2016-05-01 | 2016-05-09 |
| NCT00388388 | Pre-hypertension|Pre-diabetes | Drug: losartan, hydrochlorothiazide | Sir Mortimer B. Davis - Jewish General Hospital|Merck Frosst Canada Ltd. | Phase 2 | 2007-03-01 | 2015-05-18 |
| NCT00675987 | Obesity|Hypertension|Hyperglycemia | Drug: losartan|Drug: Placebo control | Brigham and Women's Hospital|Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Phase 4 | 2007-05-01 | 2013-02-04 |
| NCT00953680 | Hypertension | Drug: losartan potassium (+) hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)|Drug: losartan potassium|Drug: hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Phase 1 | 2004-04-01 | 2016-01-21 |
| NCT01124175 | Healthy | Drug: Losartan|Drug: Cozaar庐 | Teva Pharmaceuticals USA | Phase 1 | 2003-10-01 | 2010-11-22 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们