-
生物活性
FK-506 is an agent that binds to the immunophilin FKBP12 and inhibits PP2B (calcineurin). Potent calcineurin (protein phosphatase 2B) inhibitor that requires FK 506-binding protein 12 (FKBP12) for activity (IC50 = 3 nM). Inhibits secretion of IL-1, IL-2 (IC50 = 1 nM), IL-3, IL-4, IL-6 (IC50 = 35 nM), GM-CSF, TNFα (IC50 = 10 nM), IFNγ and Myc from activated T cells in vitro. Exhibits potent immunosuppressive, neuroprotective and anticonvulsant activity in vivo. FK-506, cyclosporin A, and rapamycin have been shown to inhibit specific transduction pathways, which results in T lymphocyte activation. The compound can also inhibit cAMP levels in the presence of carbachol. Along with cyclosporin A and rapamycin, FK-506 can bind to immunosuppressant binding proteins with high affinity. FK-506 has been found to show neuroregenerative and neuroprotective actions aside from its immunosuppressant activity. Research indicates that FK-506 can stop T cell proliferation in vitro by blocking the generation of a variety of lymphokines, in particular, interleukin (IL-2).
FK506 inhibits the replication of the prototypic Orthopoxvirus, vaccinia virus strain WR, with an IC50 of 12.05μM.[1]
FK506 inhibits transcription of the human prolactin gene (IC50 = 25 nM).[2]
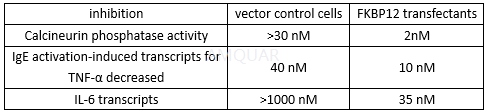
FK506 inhibits calcineurin phosphatase activity in pancreatic islet cells (IC50 = 1 nM).[3]
The cytotoxic /proliferation effects
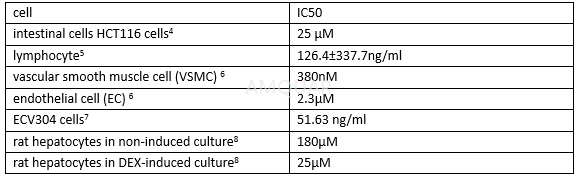
IC50 values of tacrolimus in cytokine production from human PBMC[9]
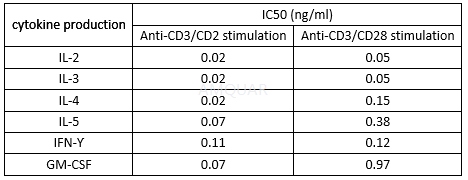
The IC50 of FK506 for inhibiting Cytokine Production
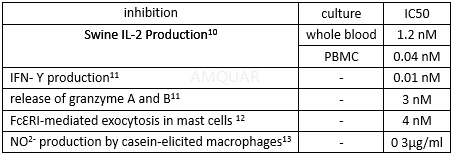
The inhibition of FK506 for cytokine in mast cells with or without overexpression of FK506 binding protein (FKBP) 12[14]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
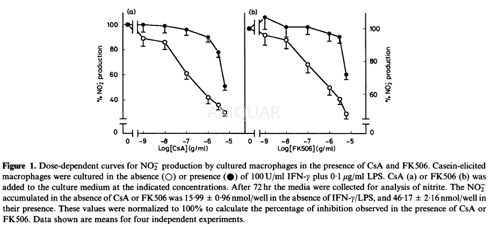
NOS activity assay[13]
The enzyme preparation was obtained from macrophages cultured with 100 U/ml IFN-Ƴand 0.1μg/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24 hr. Macrophage monolayers were detached using a rubber policeman and resuspended in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride (PMFS) (0.1 mg/ml), trypsin inhibitor (0.01 mg/ml) and leupeptin (0.01 mg/ml), at a cell density of 1 x 107cells/ml. The cells were disrupted by sonication and centrifuged at100 000 for 30 min at 4°. The supernatant was collected to assay the enzyme activity.
NOS activity was assayed following [3H] citrulline formation from [3H] arginine. Briefly, the reaction mixture (100μl) contained 100PM L-[3H] arginine (2μCi/μM), 500μM NADPH, 20μM BH4, 20μM FAD, 1 mM DTT and 1 00000g supernatant in 50 mM Tris-HC1 pH 7.4. After 60 min incubation at 370, the reaction was finished by addition of 400μlof cold-stop buffer (10mm EGTA, 100 mM HEPES, pH 5.5, and 1 mM L-citrulline). The reaction mixture was then applied to a 1-ml column of Dowex AG 50W-X4 from BDH (England) (Na+form), preequilibrated with stop buffer, which was eluted with 2ml of water. L-[3H] Citrulline was quantified by liquid scintillation.
-
细胞实验
Drugs and chemicals[4]
Tacrolimus (TAC) and Sirolimus (SRL) were dissolved in DMSO and then stored at-20oC. Cell culture medium RPMI1640, fetal calf serum (FCS), L-glutamine (200 mM), and a mixture of penicillin (100U/mL), streptomycin (100mg/ml), trypsin–EDTA (0.5/0.2mg/ml) and phosphate- buffered saline (PBS) were prepared.
Cell line and culture
The human colon cancer cell line HCT 116 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 1% L-glutamine (200mM) and 1% mixture penicillin (100 U/mL) and streptomycin (100 mg/mL) and were incubated in a humidified air/CO2 (95:5) mixture at 37oC.
Cell viability assay
Cytotoxicity of TAC and SRL was determined by MTT test. HCT116 cells (3x104cells per well) were incubated in 96-well plates with increasing concentrations of TAC (0–40μM) or SRL (0–30μM) and their combination SRL/TAC ((1/25μM) or (10/23μM)) for24 h at 37oC in a final volume of 200μL. After treatment, fresh medium (200μL) containing 1 mg/mL MTT were incubated for 4 h at 37oC in the plates. The medium was then removed and 100μL of 0.04M HCl/Isopropanol was added to each well for 1 h to dissolve the formazan. The absorbance was determined by spectrophotometer microplates reader at 560 nm. IC50 and IC30 values were defined as the concentration inducing 50% and 30%, respectively, loss of cell viability.

-
动物实验
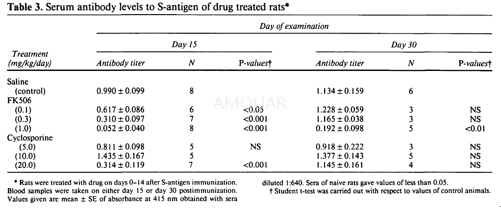
Immunization[15]
S-antigen and IRBP were prepared using bovine retinas. Myelin basic protein (MBP) purified from guinea pigs. The antigens were emulsified (1:1) in complete Freund's adjuvant, containing Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra at a concentration of 2.0 mg/ml. A total of 0.1 ml/rat, containing 30μg of S-antigen, IRBP, or MBP were injected into one hind footpad.
Drugs
FK506 was suspended in physiological saline and injected intraperitoneally. Cyclosporine was dissolved in pure olive oil and administered by intramuscular injection.
Treatment Schedule of Rats
Male rats between 8 and 12 weeks of age were used.Rats were treated with drugs daily, on days 0-14, on days 0-5, or on days 7-12, after immunization with S-antigen. Control rats were injected with physiological saline. Some of FK506-treated and EAU suppressed rats which were immunized with S-antigen on day 0 and treated with the drug on days 0-14 were reimmunized on day 30 with S-antigen, IRBP or MBP.
Evaluation of Disease Development and Systemic Condition
Clinical signs of EAU were monitored daily under the operating microscope for up to 3 weeks after immunization and up to 3 months in some rats. All eyes were examined histologically. The development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) was monitored daily according to the neurological signs. To monitor the systemic condition of rats, the body weight was measured before and after the drug treatment and the results are expressed as percent of control rats treated with physiological saline.
Evaluation of Immune Responses
Some rats were killed on the day after the termination of drug treatment (day 15) or 2 weeks thereafter (day 30). Blood samples were used to measure the levels of antibodies to S-antigen, using an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Mitotic responses of nonadherant spleen cells to S-antigen or concanavalin A were measured.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Reis SA, Moussatche N, Damaso CR. FK506, a secondary metabolite produced by Streptomyces, presents a novel antiviral activity against Orthopoxvirus infection in cell culture. J Appl Microbiol. 2006;100(6):1373-1380.
[2] Stefaan Wera AB, Joseph A. Martial. Rapamycin, FK506 and cyclosporin A inhibit human prolactin gene expression. FEBS Lett. . 1995;358(2):158-160.
more
分子式
C44H69NO12 |
分子量
804.02 |
CAS号
104987-11-3 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
110 mM |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
105 mM |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT02805842 | Medication Adherence | Drug: Tacrolimus BID|Drug: Advagraf QD | Rabin Medical Center|Astellas Pharma Inc|Teva Pharma | Phase 3 | 2016-08-01 | 2016-07-10 |
| NCT00302523 | Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy | Drug: Tacrolimus | Nanjing University School of Medicine | | 2006-03-01 | 2012-02-02 |
| NCT00302536 | Focal Glomerulosclerosis | Drug: Tacrolimus | Nanjing University School of Medicine | | 2006-03-01 | 2012-02-08 |
| NCT02608606 | Evidence of Liver Transplantation|Effects of Immunosuppressant Therapy | Drug: Tacrolimus | Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile | | 2015-03-01 | 2016-10-10 |
| NCT02794610 | Ocular Penetration of Topical Tacrolimus | Drug: Tacrolimus | The Eye Center and The Eye Foundation for Research in Ophthalmology | | 2016-05-01 | 2016-06-08 |
| NCT02444143 | Kidney Transplantation | Drug: tacrolimus extended release | University of Illinois at Chicago|Astellas Pharma US, Inc. | Phase 4 | 2015-05-01 | 2015-05-11 |
| NCT01131988 | Healthy | Drug: Tacrolimus Capsules | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2008-01-01 | 2010-06-11 |
| NCT02456025 | Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis | Drug: Topical tacrolimus | The Eye Center and The Eye Foundation for Research in Ophthalmology | Phase 4 | 2013-04-01 | 2015-11-22 |
| NCT01132027 | Healthy | Drug: Tacrolimus Capsules | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2008-01-01 | 2010-06-11 |
| NCT03020589 | Renal Transplant | Drug: Tacrolimus | University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill | Phase 4 | 2017-01-01 | 2017-03-21 |
| NCT00935298 | Renal Transplantation | Drug: Tacrolimus | The Second Artillery General Hospital|Capital Medical University|Shanghai Changzheng Hospital|Pharmacology Research Institute|Air Force General Hospital of the PLA|Health Department of General Logistics | Phase 4 | 2009-07-01 | 2011-12-21 |
| NCT01655563 | Heart Transplantation|Liver Transplantation|Kidney Transplantation | Drug: Tacrolimus | The Hospital for Sick Children | Phase 2 | 2011-09-01 | 2016-08-18 |
| NCT00492661 | Renal Transplantion|Kidney Transplantion | Drug: Tacrolimus With Diet and Exercise Intervention | Janssen-Cilag Pty Ltd | Phase 4 | 2007-07-01 | 2013-05-24 |
| NCT02014103 | Complication of Transplant | Drug: Tacrolimus | University of Cincinnati|University of Colorado, Denver|Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati | Phase 4 | 2015-03-01 | 2016-03-11 |
| NCT01476488 | Kidney Transplantation|Pediatric Patients|Maintenance With Tacrolimus | Drug: tacrolimus | Seoul National University Hospital | Phase 2|Phase 3 | 2011-07-01 | 2015-05-24 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们