-
生物活性
Atorvastatin Calcium Salt is a selective and competitive HMGCR (HMG-CoA reductase) inhibitor (IC50 = 8 nM), the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase results in a drastic reduction in the production of cholesterol and other isoprenoids. Competitive inhibitors of the reductase are believed to induce the expression of LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein) receptors in the liver, which in turn increases the catabolism of plasma LDL and lowers the plasma concentration of cholesterol.Reduces circulating LDL-C by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis and inducing expression of LDL receptors. Inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in vitro and exhibits antinociceptive effects in the inflammatory hypernociception model.
The inhibition constant values of HMG-CoA reductase for atorvastatin is 8 nM[1]

Activity in the duration of the plateau of human atrial action potentials[4]
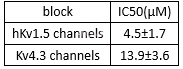
Atorvastatin activity in human SV-SMC (saphenous vein smooth muscle cell) [5]
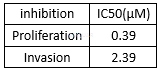
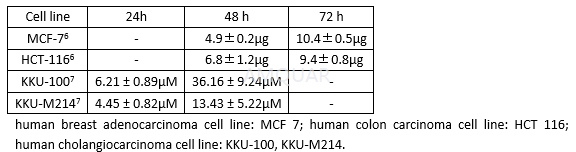
IC50 values of atorvastatin at different time intervals for cancer cell lines
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
5% DMSO+castor oil
-
激酶实验
HMG-CoA reductase activity determination[8]
The calcium precipitation technique was used to prepare endoplasmic reticulum, and the microsomal protein concentrations were determined by the Lowry method. Incubations for enzyme assay were carried out in a total volume of 150 μL, which contained 0.1–0.8 mg of microsomal protein, 2mmol/L, NADPH, 30mmol/L glucose-6-phosphate, 1.75IU/mL glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and 0.2mmol/L HMG-CoA. The reaction time was 45 min, and the samples were incubated for another 30 min at 37 °C to allow complete lactonization of mevalonate. Then mevalonolactone was isolated from the incubation mixture by two successive extractions with 7.5 mL benzene. A 10 mL aliquot of the pooled benzene extracts was transferred to a cryovial and dried at –56 °C in a freeze-drier. Dried mevalonolactone was dissolved in high performance liquid chromatogram (HPLC)-grade water, and the concentration was determined using HPLC. Chromatographic separations were carried out using an Agilent ZORBA Extend-C18 column (4.6×1.50 cm inner diameter, 3.5 μm). Aliquots (100μL) of each sample were injected into the HPLC system. The mobile phase consisted of HPLC-grade water, and the elution was carried out at 1 mL/min at 37 °C. The detection was carried out at 200 nm. HMG-CoA reductase activity was determined by calculating the concentrations of mevalonolactone and expressed as units per gram of protein (1 unit yields 1 μmol of product per min).
-
细胞实验
Isolation and culture of VSMCs[9]
Rat aortic SMCs were isolated from thoracic aortas of male Sprague-Dawley rats by using the collagenase digestion method, and cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 mg/mL streptomycin at 37.0°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. For all experiments, primary rat aortic VSMCs were subcultured and used between passages 4 to 7. VSMCs were grown to 70% to 80% confluence and then made quiescent by incubation in DMEM without FBS for 24 hours before experiments.
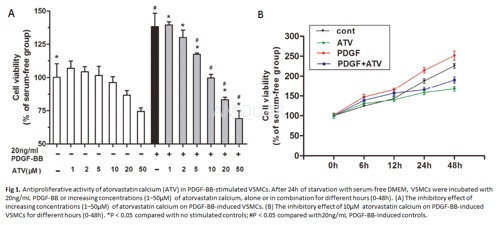
Cell Stimulation by PDGF-BB and Treatment of atorvastatin calcium
VSMCs were grown to 70–80% confluence and pre-cultured in serum-free medium for 24h before treatment. Atorvastatin calcium was dissolved in methanol for a stock solution of 100mM and then diluted to desired concentrations with media prior to cell treatment. Cells were treated with various concentrations of atorvastatin calcium from 1 to 50μM in cell proliferation assay, 10μM in migration assay, cell morphology and western blotting on quiescent cells with or without 20ng/mL PDGF-BB for designated times.
Cell Proliferation and DNA Synthesis
MTT assay
VSMCs were cultured to 80% confluence and serum-free for 24 hours. Cell viability was examined by MTT assay. Cells were seeded in 96-well culture plates at a density of 5000/well and incubated with 0.5mg/mL MTT in the last 4h of the culture period at 37°C. Thereafter, the medium was replaced with 100 μl DMSO and the plate was gently rotated on a linear and orbital shaker for 5 min to completely dissolve the precipitation. An automatic microplate reader microplate reader) was used to determine the absorbance at 570 nm.
Edu incorporation assay
Cells were incubated with Edu-labeling solution for 2h at 37°C, and then the cells were fixed with 4% cold formaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature. After permeabilization with 1% Triton X-100, the cells were reacted with Click-iT1 reaction cocktails for 30 min. Subsequently, the DNA contents of the cells were stained with Hoechst 33342 for 30 min. Finally, Edu-labeled cells were counted using fluorescence microscopy and normalized to the total number of Hoechst-stained cells.
-
动物实验
Animals – study design[10]
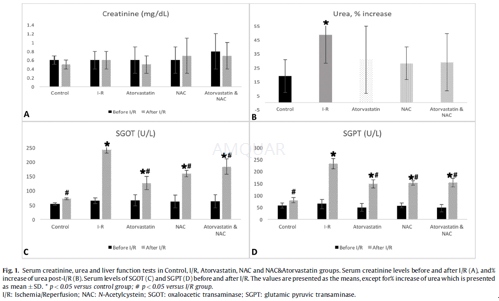
10-week-old Wistar male rats and 220–250 g in weight were obtained and maintained in weather controlled chambers (temperature 23±2oC, humidity 55±5%) under controlled lightning (12 h light per day) and central ventilation (15 air changes/h) for 15 days in order to adapt to the new environment. Normal chow diet consisted of ELVIZ 510 food pellets which contained a full nutrient supplementation and were provided ad libitum. All possible precautions were taken to avoid animal suffering at each stage of the experiment. Rats had free access to food and water throughout the study. Forty rats (n = 40) were randomized into 5 experimental groups as follows: Control group: animals were subjected to laparotomy without vascular occlusion (sham surgery) (n = 8); Ischemia-Reperfusion group (I/R): animals were subjected to 45 min of intestinal ischemia and were sacrificed 3 h after reperfusion (n = 8); Ischemia- Reperfusion plus Atorvastatin group (Atorvastatin): animals received atorvastatin pretreatment with a dose of 10 mg/kg by oral gavage 24 h before intestinal ischemia-reperfusion(n = 8); Ischemia- Reperfusion plus NAC group (NAC): NAC pretreatment was administered with a dose of 160 mg/kg by oral gavage 24 h prior to intestinal ischemia-reperfusion (n = 8); Ischemia- Reperfusion plus Atorvastatin and NAC group (Atorvastatin & NAC): combined NAC and atorvastatin pretreatment were given at the above mentioned doses by oral gavage 24 h prior to intestinal ischemia-reperfusion (n = 8).
Surgical procedure
Rats were fasted for 12 h with free access to tap water before surgery. Following local abdominal skin sterilization with Betadine 10% solution, general anesthesia was induced with 1% propofol with a dose of 100 mg/kg introduced intraperitoneally. A large median abdominal incision was performed, and the blood supplyto the intestine was interrupted for 45 min by occlusion of SMA with a microvascular clamp. Intestinal ischemia was confirmed by observing the loss of pulsation of the mesenteric artery and its branches, as well as paleness of the jejunum and ileum. The laparotomy incision was covered with sterile moist swabs during the ischemia period. Following 45 min of ischemia, blood perfusion to intestinal tissue was released, and the reperfusion phase was allowed for 3 h. The intestine returned to the abdomen, and the abdominal wall was closed. In the control group (sham), SMA was exposed but not occluded and animals were followed for 45 min to simulate the ischemic interval. The reperfusion interval was simulated, and the animals were then subjected to the same procedures.
At the end of the reperfusion phase, the rats were reanaesthetized and the abdomen re-opened in order to obtain liver and right kidney tissue samples. After the sampling procedure, the animals were euthanized.
Blood collection – serum measurements
Blood samples were collected before surgery (t0) and during euthanasia (t1) (at 9:00 AM, after a 12-h fast) using capillary tubes introduced into the medial retroorbital venous plexus. The serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 min.
Serum concentrations of creatinine, urea, SGOT and SGPT were determined using the enzymatic PAP commercial kit
ELISA measurements
TNF-a, IL-6, IL-1b and ICAM-1 levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using commercially available kits (Intra Assay CV < 10%, Inter Assay CV < 12%). Samples were run in 96 well plates on a plate reader to determine absorbance at 450 nm.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Istvan ES DJ. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001;292(5519):1160-1164.
[2] Parquet V, Henry M, Wurtz N, et al. Atorvastatin as a potential anti-malarial drug: in vitro synergy in combinational therapy with quinine against Plasmodium falciparum. Malar J. 2010;9:139.
more
分子式
C66H68CaF2N4O10 |
分子量
1155.34 |
CAS号
134523-03-8 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
100 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
23 mg/mL
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT01645410 | Healthy | Drug: Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets, 40 mg | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2009-03-01 | 2012-07-19 |
| NCT01645384 | Healthy | Drug: Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets, 40 mg | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2009-05-01 | 2012-07-19 |
| NCT01555632 | Recurrent Prostate Cancer|Stage I Prostate Cancer|Stage IIA Prostate Cancer|Stage IIB Prostate Cancer|Stage III Prostate Cancer|Stage IV Prostate Cancer | Drug: atorvastatin calcium|Drug: placebo | University of Nebraska|National Cancer Institute (NCI) | | 2012-03-01 | 2013-06-17 |
| NCT01645423 | Healthy | Drug: Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets, 80 mg | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2009-08-01 | 2012-07-19 |
| NCT01645449 | Healthy | Drug: Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets, 80 mg | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited | Phase 1 | 2010-06-01 | 2012-07-19 |
| NCT01964326 | Hypercholesterolemia | Drug: Atorvastatin calcium 10 mg | Pfizer | Phase 3 | 2013-10-01 | 2016-04-18 |
| NCT01665677 | Graft vs Host Disease | Drug: Atorvastatin calcium | Mehdi Hamadani|West Virginia University|Medical College of Wisconsin | Phase 2 | 2012-09-01 | 2016-12-14 |
| NCT01431105 | Kawasaki Disease | Drug: Atorvastatin | University of California, San Diego|Children's Hospital Colorado|University of Colorado, Denver | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2012-07-01 | 2016-10-25 |
| NCT00185731 | Leukemia|Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin | Drug: Atorvastatin | Dean Felsher|The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society|Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation|Burroughs Wellcome|Stanford University | Phase 2 | 2005-04-01 | 2013-03-07 |
| NCT01306565 | Cardiovascular Disease | Drug: Low dose Atorvastatin|Drug: High dose atorvastatin | Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences | | 2009-01-01 | 2011-03-01 |
| NCT03079115 | Carotid Artery Stenosis | Drug: High-dose Atorvastatin|Drug: Conventional-dose Atorvastatin | Beijing Hospital | Phase 4 | 2017-05-01 | 2017-03-08 |
| NCT00973986 | Coronary Heart Disease | Drug: Atorvastatin | Liuhuaqiao Hospital|Guangdong Province, Department of Science and Technology | Phase 1 | 2009-06-01 | 2011-11-28 |
| NCT00435045 | Hypertriglyceridemia | Drug: Lovaza (omega-3-acid ethyl esters) [formerly known as Omacor] plus atorvastatin|Drug: atorvastatin | GlaxoSmithKline | Phase 3 | 2007-02-01 | 2016-12-02 |
| NCT02901379 | Myocardial Edema | Drug: Atorvastatin 80mg|Drug: Atorvastatin 10mg | National Cardiovascular Center Harapan Kita Hospital Indonesia | Phase 3 | 2016-10-01 | 2016-09-14 |
| NCT02370784 | Scleroderma | Drug: atorvastatin|Drug: Placebo | University of Pittsburgh|National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) | Phase 2 | 2015-02-01 | 2015-12-01 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们























