-
生物活性
Rapamycin is a macrolide compound that is used to coat coronary stents, prevent organ transplant rejection and to treat a rare lung disease called lymphangioleiomyomatosis. It has immunosuppressant functions in humans and is especially useful in preventing the rejection of kidney transplants. It inhibits activation of T cells and B cells by reducing the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2).
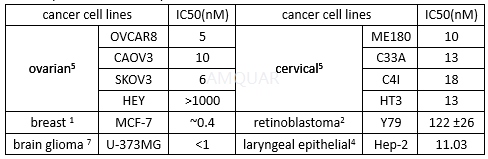
The antiproliferative activity in cancer cell line
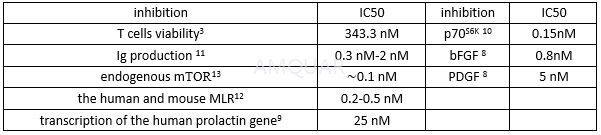
The inhibition of rapamycin
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
0.5% CMC+0.25% Tween 80
-
激酶实验
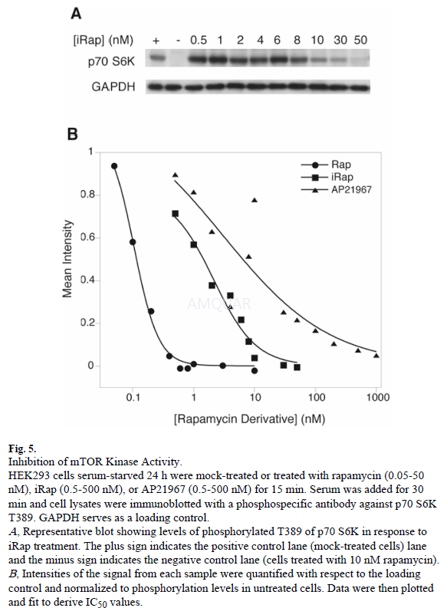
Immunoblotting for the mTOR Kinase Assay[13]
HEK293 cells were plated at 2-2.5 × 105 cells per well of a 12-well plate and serum-starved for 24 h in DMEM only. Cells were mock-treated or treated with rapamycin (0.05-50 nM), iRap (rapamycin analog) (0.5-500 nM), or AP21967 (0.5-500 nM) for 15 minutes at 37 °C. Serum was added to a final concentration of 20% for 30 minutes at 37 °C. Cells were lysed and cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE. Resolved proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane and immunoblotted with a phosphospecific primary antibody against Thr389 of p70S6K. Data were analyzed using ImageQuant and KaleidaGraph.
-
细胞实验
Cell lines and Culture[1]
The MCF-7 or Human Breast Adenocarcinoma cancer cell line was used throughout this study.Stock culture of MCF-7 cells was grown in T25-cm2 tissue culture flasks in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) as a differentiation media, supplemented with 0.5% (v/v) fetal bovine serum, and 1% (v/v) penicillin and streptomycin. The cells were passaged upon reaching a confluency of >80%, and were split at different ratios based on the experiments being performed. Cultures were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The cells were passed twice a week.
IC50 determination
MCF-7 cells were plated at a density of 1 x 105cells/ well in 6-well plates. After 24h, cells were treated with a series of concentrations of Rapamycin with DMEM medium was only added to the untreated division. These cells were subsequently grown at 37oC, 5% CO2and 95% air for 72h. To determine cell viability, the trypan blue exclusion assay was used using 20μl of cell suspension in DMEM medium which were mixed with 20μl of trypan blue. The numbers of stained (dead cells) and unstained (live cells) cells were subsequently counted using a hemocytometer.
Cell proliferation assay
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density of 1x105cells/well. After 1 day, rapamycin at IC50 concentration was added into the wells. Untreated were exposed to culture medium without rapamycin. Then, the cells were further incubated for 8 days. Cell proliferation was evaluated using a trypan blue exclusion method. Cells were counted every day until the eighth day to identify the growth pattern of the treated and untreated cells. Results were expressed as a percentage of the control.
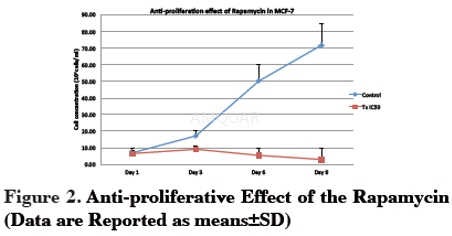
-
动物实验
Tumor Cell Lines[6]
The cell lines U-87was maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium/F12 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. The cell lines tested negative for Mycoplasma contamination. U-87 expresses high constitutive levels of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1,4 resulting in enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
Drugs
Rapamycin was stored at a concentration of 5 mg/ml in 100% ethanol at –20°C and was diluted in serum-free medium immediately prior to use.
Murine Models and Tumor Formation
All animal studies were conducted with a protocol approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees. Male 6- to 8-week-old nude mice were housed within an approved specifi c pathogen–free barrier facility maintained at the M.D. Anderson Isolation Facility in accordance with Laboratory Animal Resources Commission standards. Appropriate measures were taken to minimize animal discomfort, and appropriate sterile surgical techniques were utilized in tumor implantation and drug administration. Animals that became moribund or had necrotic tumors were compassionately euthanized.
To induce the subcutaneous tumors, logarithmically growing U-87 cells were injected into the right hind flank of nude mice at a dose of 1 x 106cells per 200μl. Treatment with rapamycin intraperitoneally at a dose of 1.5 mg/kg/day was begun when the majority of animals had palpable tumors (at day 5). Tumors were measured every other day, and tumor volumes (length x width2/2) were calculated on the basis of the tumors that grew in surviving mice. 
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Tengku Din TADA-A, Seeni A, Khairi W-NM, Shamsuddin S, Jaafar H. Effects of Rapamycin on Cell Apoptosis in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 2015;15(24):10659-10663.
[2] Yan-Dong Wang Y-JS, Jian-Ying Li, Xiang-Chao Yao, Guang-Jiang Liang. Rapamycin, a mTOR inhibitor, induced growth inhibition in retinoblastoma Y79 cell via down-regulation of Bmi-1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):5182-5188.
more
分子式
C51H79NO13 |
分子量
914.18 |
CAS号
53123-88-9 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
25 mg/mL |
Water
Insoluble |
Ethanol
50 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
约30 mg/mL
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT00555256 | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Drug: sunitinib and rapamycin (Drug will be held) | Washington University School of Medicine|Pfizer | Phase 1 | 2007-11-01 | 2016-05-05 |
| NCT01063478 | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Drug: RAD001 (in addition to standard radiation and chemotherapy) | University of Chicago|Novartis Pharmaceuticals | Phase 1 | 2010-02-01 | 2014-01-16 |
| NCT00823459 | Low-grade Glioma|Astrocytoma|Oligodendroglioma|Mixed Oligoastrocytoma | Drug: RAD001 | University of California, San Francisco | Phase 2 | 2009-01-01 | 2016-02-16 |
| NCT00779194 | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | Drug: Rapamycin | State University of New York - Upstate Medical University|Pfizer | Phase 2 | 2008-10-01 | 2016-10-12 |
| NCT01060605 | Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 | Drug: rapamycin | IRCCS San Raffaele|Ministry of Education, Universities and Research, Italy|Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation|Telethon-JDRF Center for Beta cell replacement: clinical core. | Phase 3 | 2001-10-01 | 2010-02-01 |
| NCT00450320 | Sarcoma | Drug: sirolimus | AIDS Malignancy Consortium|National Cancer Institute (NCI)|The EMMES Corporation | Phase 1 | 2007-10-01 | 2014-08-27 |
| NCT00920309 | Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease | Drug: Rapamycin|Other: Standard of Care-Placebo | Yale University | Phase 2|Phase 3 | 2009-06-01 | 2014-03-07 |
| NCT01526356 | Angiofibromas|Tuberous Sclerosis | Drug: Placebo|Drug: Rapamycin|Drug: Rapamycin | The University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston | Phase 2 | 2012-05-01 | 2015-06-09 |
| NCT01014234 | Kidney Transplantation | Drug: Cyclosporins|Drug: Rapamycin | IRCCS Policlinico S. Matteo | Phase 2 | 2008-07-01 | 2015-03-24 |
| NCT00928798 | Birt-Hogg-Dub茅 Syndrome | Drug: Rapamycin|Drug: placebo | Maastricht University Medical Center|Myrovlytis Trust | Phase 3 | 2010-01-01 | 2012-03-07 |
| NCT01709136 | Hypertension | Drug: Sirolimus | University of Pittsburgh | Phase 2|Phase 3 | 2005-12-01 | 2016-03-21 |
| NCT00446368 | Carcinoma, Renal Cell | Drug: RAD001 | The Methodist Hospital System|Novartis | Phase 2 | 2005-05-01 | 2016-03-15 |
| NCT02753309 | Bladder Cancer | Drug: Sirolimus | The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio | Early Phase 1 | 2016-06-01 | 2016-09-01 |
| NCT01827618 | Invasive Bladder Cancer Stage II | Drug: Rapamycin | The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio | Early Phase 1 | 2012-04-01 | 2015-06-30 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们