-
生物活性
Lenalidomide is nearly 2000 times more potent than thalidomide as a TNF-α inhibitor in vitro. The inhibition in LPS Stimulated Human PBMC and Whole Blood: TNF-α Inhibit at 100 μM is 74%; IC50 for TNF-α is 100 nM; IC50 for Whole Blood TNF-α is 480 nM.
-
体外研究
Lenalidomide disrupts the MM/BMSC cell cross-talk, by inhibiting TNF-α-induced adhesion molecules (VLA-4, LFA-1, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) expression on both MM and stromal cells, as well as cytokine secretion (i.e. IL-6, TGF-β and IGF-1) and VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. Lenalidomide blocks myeloma progression through activating NK cells and disrupting PD-L1/PD-1 axis.[1] Lenalidomide was substantially more effective at reducing Cereblon–Rabex-5 binding than either thalidomide or pomalidomide, Besides, there is potential for an IMiD-sensitive relationship between Cereblon and Rabex-5, which in turn has the potential to contribute to the antiinflammatory properties of IMiDs.[2] Lenalidomide displayed a strong therapeutic effect in several experimental murine models of autoimmune/inflammatory diseases: 2, 4, 6- trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid- and dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammatory bowel disease and type II collagen-induced arthritis.[3] Lenalidomide causes a dose/time-dependent degradation of CK1α protein with a subsequent reduction of its kinase activity. And the inhibition/silencing reinforce lenalidomide cytotoxicity.[4] Lenalidomide sensitivity is independent of cytogenetic subtype in HMCLs. However CRBN and IRF4 have been shown to be associated with response to lenalidomide.[5] High level of CRBN is required for the anti-MM activity of lenalidomide, since My5.LV cells, which express lower levels of CRBN, were resistant to lenalidomide. Whereas My5.CRBN. His cells, which express higher levels of CRBN, were sensitive to lenalidomide.[6] The expansion of poly functional NK cells against target cells, including CD138+ myeloma cells from MM patients, could be enhanced by lenalidomide via a putative early apoptotic NK cells rescuing effect. Besides, the effect is increased in the presence of polyIgs and PL.[7] LEN significantly enhances antitumor functions of CAR19 and CAR20 T cells in vivo. Additionally, it enhances production of interferon gamma by CAR19 T cells and augments cell signaling via CAR19 protein in T cells in vitro. Besides, LEN works through direct effects on T cells but not on B-NHL cells.[8] Lenalidomide enhances myeloma-specific T-cell responses in vivo and in vitro.[9] Lenalidomide exerts diverse immunomodulatory effects on lymphoma B cells and CD4+CD25+Tregs and in addition modulates their mutual interactions. In another words, lenalidomide interferes with signals inducing Treg proliferation, but does not directly inhibit proliferation of Tregs that have been previously activated in the absence of lenalidomide.[10] LEN induced GPR68 expression via IKAROS family zinc finger 1 (IKZF1), resulting in increased cytosolic calcium levels and activation of a calcium-dependent calpain, CAPN1, which were requisite steps for induction of apoptosis in MDS cells and in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells.[11] Lenalidomide Induces Interleukin-21 Production by T Cells and Enhances IL21-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B Cells.[12] Lenalidomide has E3 ubiquitin ligase inhibitory effects that extend to RNF41 and that inhibition of RNF41 auto-ubiquitination promotes membrane accumulation of signaling competent JAK2/EpoR complexes that augment Epo responsiveness.[13] Lenalidomide targets the generation, but not the survival of long-lived plasma cells. During plasma cell differentiation, lenalidomide affects minimally the formation of human PBs, specifically targets the generation of prePBs from MBCs, of early PCs from PBs and of LLPCs from early PCs, and does not alter the survival of LLPCs once generated.[14] Combined with 5-AzaC, lenalidomide enhances the ability of DC to stimulate T-cell proliferation in mixed leukocyte reaction and increases secretion of IL-12 and IL-15 by DC.[15]
-
体内研究
30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol
-
激酶实验
Assay for inhibition of TNF synthesis by human PBMCs[17]
Human PBMCs from normal donors were obtained by Ficoll-Hypaque (Pharmacia Fine Chemicals, Piscataway, NJ) density centrifugation. Cells (106cells/mL) were cultured in RPMI (Gibco Laboratories, Grand Island, NY) supplemented with 10 AB+ serum (Biocell, Rancho Dominguez, CA), 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco). Test compounds were dissolved in DMSO (Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO) at 20 mg/mL; further dilution was done with culture medium. The final DMSO concentration in all assays including the controls was 0.25%. Test compounds were added to cells 1 h prior to the addition of LPS. PBMCs (106cells/mL) were stimulated with 1μg/mL of LPS from Salmonella minnesota R595 (List Biological Labs, Campbell, CA). Cells, in triplicate, were incubated with LPS for 18-20 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2. Supernatants were then harvested and assayed for cytokine levels. In some experiments, supernatants were kept frozen at -70 °C until use. Cell viability was assayed by Trypan blue exclusion dye method. The concentration of TNFαin the culture supernatants was determined by ELISA (ENDOGEN, Boston, MA) according to the manufacturer’s directions. All compounds were assayed in a minimum of three separate experiments. Percent inhibition was determined as 100 × [1 - (cytokine(experimental)/cytokine(control))].
-
细胞实验
Cells, media and antibodies[8]
HEK and Ramos cell lines were grown in IMDM media supplemented with 10% FCS, antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin) and were mycoplasma negative. Following fluorochrome labeled antibodies were used: Alexa 647 goat antimouse(Jackson Immuno), pacific Blue anti-CD4C, PerCP anti- CD8C, APC anti-CD69, PE anti-CD19 and PE anti-CD20 (all Exbio), for stimulation and western blotting were used unlabeled antibodies specific for: CD3, CD28 (MiltenyiBiotec), TCRzeta (Santa Cruz), Aiolos, Ikaros, pERK, total ERK (all Cell Signaling).
Cell activation,lenalidomidetreatment
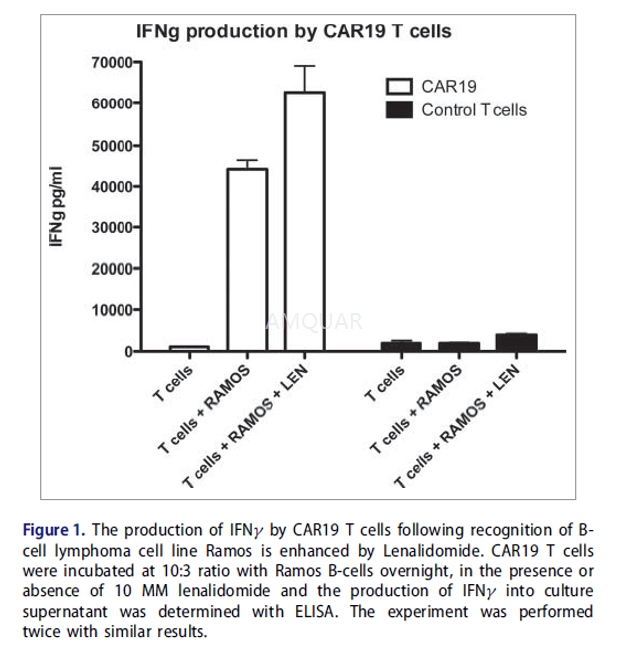
Goat anti-mouse polyclonal serum (Jackson Immuno), or anti-CD3 antibody MEM-57 were adsorbed onto plastic plates at 37oC for 1 h, washed with PBS and then used for stimulation of CAR19 T cells. T cells and B cells were incubated for 24 h in the presence 10MM LEN in culture media (without IL2), cells were then centrifuged twice to wash out excess of LEN and used for in vitro assay.
Interferon gamma assay
The concentration of IFNƳ was determined by ELISA assay kit (Biolegend), the absorbances were read with ELISA plate reader at wavelengths specified in the kit. For the assay, we usually incubated 10,000 T cells with 3,000 B cells, in 100 uL of media for 12 h without the presence of IL2, before analysis cells were freeze-thawed. The concentration of IFNƳ was calculated in Prism software according to the dilution of IFNƳstandard.
-
动物实验
Induction and treatmentof collagen-induced arthritis[3]
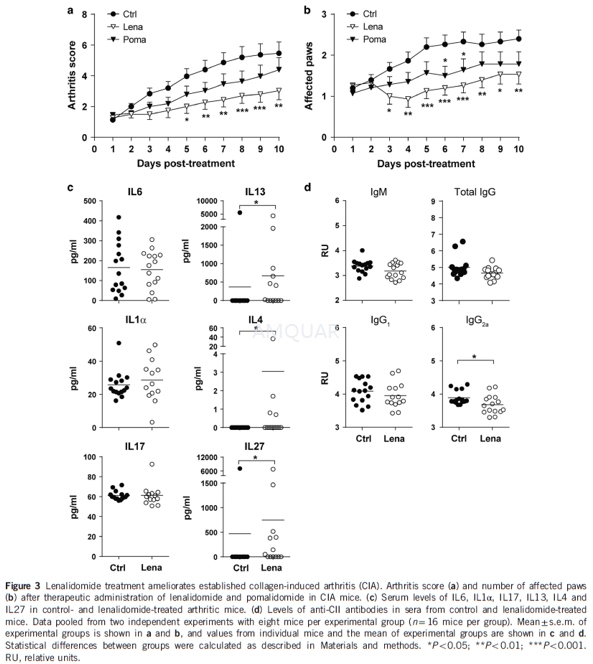
DBA/1OlaHsd mice were purchased from Harlan Laboratories and housed under specific pathogen-free conditions. Ten-week-old male mice were immunized by intradermal injection at the base of the tail with 200 μg of chicken CII in complete Freund’s adjuvant as described. Lenalidomide and pomalidomide (50 mg kg− 1) or PBS-1% DMSO (vehicle, control mice) were administered daily by i.p. injection starting on the day of arthritis onset. Arthritis severity was graded daily for each paw by two independent observers using the following scoring system: 0=normal, 1=slight swelling and erythema, 2=pronounced edematous swelling and 3=stiffness of the joint. This yielded a maximum score of 12 per mouse. Disease severity was expressed as mean clinical score±s.e.m. per group of treatment. Sixteen mice per group were included, eight in each experiment. All animal procedures were approved by the Hospital 12 de Octubre Animal Welfare Committee.
Serum measurements
Serum was collected from mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) after 10 days of treatment. Serum anti-CII-specific antibodies IgM, total IgG, IgG1 and IgG2a subclasses were determined by ELISA in96-well ELISA plates coated with CII (2 μgml− 1 in Tris buffer (0.05 M Tris, 0.2 M NaCl, pH 7.4) and horseradish peroxidase-coupled goat anti-mouse Ig class-specific antibodies. Relative antibody units (RU) were calculated as the log10 of the reciprocal of the dilution giving50% of maximal optical density. Serum IL6 levels were assessed by ELISA (Mouse IL-6 ELISA MAX Standard; BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA). Serum levels of IL1α, IL17, IL13, IL4, IL27 were assessed by FlowCytomix Multiple Analyte Detection System (Mouse 13plex kit FlowCytomix, eBioscience, Vienna, Austria).
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Massimo Giuliani BJ, Guy Berchem. Activation of NK cells and disruption of PD-L1/PD-1 axis: two different ways for lenalidomide to block myeloma progression. Oncotarget. 2017;Advance Publications.
[2] Millrine D, Tei M, Gemechu Y, Kishimoto T. Rabex-5 is a lenalidomide target molecule that negatively regulates TLR-induced type 1 IFN production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(38):10625-10630.
more
分子式
C13H13N3O3 |
分子量
259.26 |
CAS号
191732-72-6 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
≥52 mg/mL at 25 °C |
Water
<1 mg/mL at 25 °C |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL at 25 °C |
体内溶解度
5 mg/mL
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT02371577 | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | Drug: Lenalidomide | University of California, San Diego|Celgene Corporation | Phase 2 | 2017-02-01 | 2016-09-26 |
| NCT02279654 | Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) | Drug: Lenalidomide | Celgene Corporation | | 2014-12-01 | 2016-11-04 |
| NCT02370888 | Leukemia, Myeloid|Myelodysplastic Syndromes | Drug: Lenalidomide | University of Florida|Celgene Corporation | Phase 1 | 2015-11-01 | 2016-11-16 |
| NCT02126553 | Leukemia | Drug: Lenalidomide | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|Celgene | Phase 2 | 2014-11-01 | 2016-11-28 |
| NCT01264315 | Multiple Myeloma | Drug: Lenalidomide | Fondazione Neoplasie Sangue Onlus | Phase 2 | 2008-09-01 | 2016-02-05 |
| NCT01582776 | Follicular Lymphoma Patients (Phase IB)|Follicular and Agressive (DLBCL&MCL) B-cell Lymphoma Patients (Phase II) | Drug: Lenalidomide and GA101 | The Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation | Phase 1|Phase 2 | 2012-10-01 | 2017-01-09 |
| NCT02371590 | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Drug: Lenalidomide|Drug: Obinutuzumab | University of California, San Diego|Celgene Corporation|Genentech, Inc. | Phase 2 | 2017-12-01 | 2017-03-13 |
| NCT02538965 | Leukemia, Myeloid | Drug: Lenalidomide | Celgene | Phase 2 | 2015-11-01 | 2017-01-27 |
| NCT01553786 | T-cell Lymphoma | Drug: Lenalidomide | The Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation | Phase 2 | 2011-11-01 | 2016-05-20 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们