-
生物活性
Fludarabine is a prodrug converted to free nucleoside 9-β-D-arabinosyl-2-fluoroadenine (F-ara-A). F-ara-A enters cells and accumulates as 5′-triphosphate. Interferes with DNA synthesis and repair.
Antiproliferative activity against human tumor cell lines invitro.[16][17]
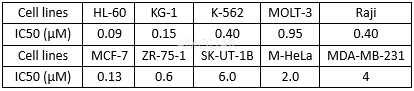
Cytotoxicity on different human cancer cell linesinvitro.[18]

-
体外研究
Fludarabine administrated in early stage of cerebral ischemia had neuroprotective effects, and the underlying mechanism could be mediated through inhibiting STAT1 phosphorylation and activating the cross regulation between STAT1 and STAT3 in neural cells.[1] Fludarabine inhibits DNA synthesis in proliferating cells. However, in indolent cells fludarabine has an inhibitory effect on RNA transcription, thus playing a major role in Multiple myeloma (MM). The mechanisms of fludarabine cytotoxicity in myeloma cell lines are related to cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis, which appears to be regulated by multiple pathways including Akt and IAP family, and activation of caspases.[2] For example, fludarabine can significantly inhibit the growth of MM cells by activating caspase-3 and inducing apoptosis of MM cells.[3] Fludarabine reduces the p21 protein level via up-regulating p53 in EHEB cells and JVM-2 cells.[4] Fludarabine causes the retention of miR-485-3p, a side effect, because of the sensitivity of the high intracellular level of miR-485-3p.[5] Fludarabine inhibited the repair of interstrand cross-links and intrastrand adducts induced by CDDP and that combined fludarabine and CDDP produced synergistic cytotoxicity in apoptosis-resistant. It means fludarabine may have a role as a DNA-repair modulator.[6] Fludarabine induces apoptosis of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected T cells via inhibition of the NF-КB signal pathway. That is to say, fludarabine may be useful for treatment of individuals with Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) and other types of cancer in which NF-КB plays a role.[7] Fludarabine induces growth arrest and apoptosis of cytokine-or alloantigen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and decreases production of Th1 cytokines via inhibition of NF-КB.[8] Fludarabine prevents smooth muscle proliferation in vitro and neointimal hyperplasia in vivo through specific inhibition of STAT-1 activation.[9] Fludarabine reduces survivability of HepG2 cells via VEGF signaling under hypoxia.[10] Fludarabine suppresses Osterix transcript levels and Osterix promoter activity, and significantly increase bone formation in a heterotopic ossification model.[11] Fludarabine markedly reduced expression of the chemokine INF-Ƴ-induced protein 10 kDa (IP-10) and the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 in a TLR4-dependent manner as well as IFN and LPS-dependent adhesion of U937 cells to endothelial cells.[12][13] Inhibition of STAT-1 activation with fludarabine reversed Bcl-2 down-expression and led to a significant decrease in apoptosis in TNF-α- and IFN-γ-treated NIT-1 cells.[14] Fludarabine-loaded RBC can selectively eliminate macrophage reservoirs and can be successfully combined with the classical antiretroviral drugs.[15]
-
体内研究
30% Propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W(5%葡萄糖水溶液)
-
激酶实验
-
细胞实验
Cell culture[7]
HTLV-1-infected T-cell lines, MT-1, MT-2 and MT-4, were kind gifts of I Miyoshi (Kochi Medical School, Kochi, Japan). HUT102 cells were generously provided by Y Maeda (Kinki University School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan). Cells were suspended in standard RPMI 1640 medium (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum.
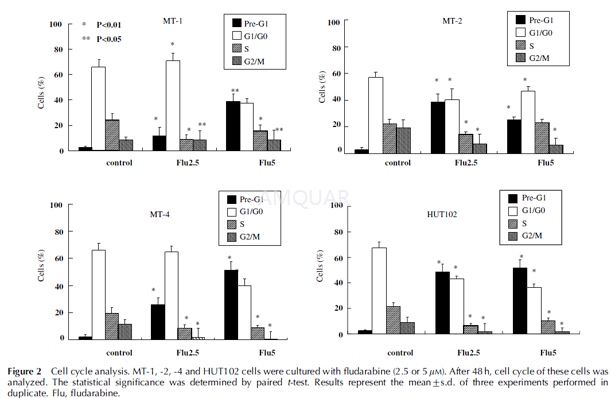
Cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry[7]
Cell cycle analysis was performed on HTLV-1-infected cells incubated with fludarabine (2.5 or 5 mM) for 2 days at5 x 105 cells/ml in 12-well plates (Flow Laboratories, Irvine, CA, USA). After incubation, cells were collected, fixed in chilled methanol and suspended in solution containing RNase A (100 U/ml, Sigma) before staining with 50 mg/ml propidium iodide. A minimum of 10 000 cells were measured using FACSCalibur apparatus (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and was analyzed using the CellQuest software package (Becton Dickinson).
-
动物实验
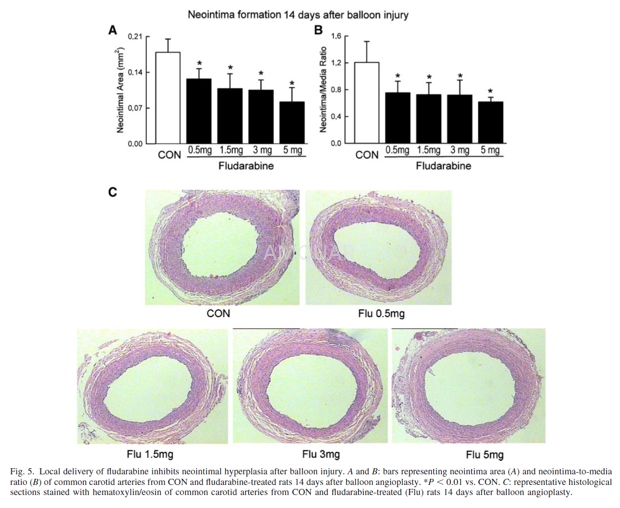
Balloon injury and local delivery of fludarabine[9]
The animals in this study were handled according to the animal welfare regulation of the Magna Graecia University of Catanzaro, and the protocol was approved by the animal use committee of this institution. Fifty Wistar rats weighing 340 ± 40 g (Charles River, Calco, Italy) were anesthetized with an intramuscular injection of 100 mg/kg ketamine (Sigma Chimica, Milan, Italy) and 5 mg/kg xylazine (Sigma Chimica). Angioplasty of the common carotid artery was performed using a balloon embolectomy catheter. Fludarabine was dissolved in 30% pluronic F127 gel (Sigma) to the final concentrations of 2.5, 5, 15, or 25 mg/ml. At the time of balloon injury, gel containing fludarabine or vehicle was applied around the middle segment (2 cm in length) of the right injured carotid artery (0.1 ml per 1-cm length of the artery segment, equivalent to 0.5, 1, 3, or 5 mg of total fludarabine locally delivered), as previously described (8, 13). As a control experiment, 200μl of fludarabine/gel solution (25 mg/ml) were applied around the sham-operated carotid artery. To study the fludarabine toxicity, laboratory studies were performed at baseline and 2 weeks after drug local delivery (25 mg/ml). Arterial pressure and heart rate were measured indirectly by a tail-cuff plethysmographic technique (model 50-0002, Harvard Apparatus, South Natick, MA).
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Xu Q, Jiang C, Rong Y, Yang C, Liu Y, Xu K. The effects of fludarabine on rat cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 2015;55(2):289-296.
[2] Meng H, Yang C, Ni W, Ding W, Yang X, Qian W. Antitumor activity of fludarabine against human multiple myeloma in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Haematol. 2007;79(6):486-493.
more
分子式
C10H12FN5O4 |
分子量
285.23 |
CAS号
21679-14-1 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
57 mg/mL at 25 °C |
Water
<1 mg/mL at 25 °C |
Ethanol
<1 mg/mL at 25 °C |
体内溶解度
约30 mg/mL
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT02649764 | Leukemia | Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: Cytarabine|Drug: LY2606368 | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|Eli Lilly and Company | Phase 1 | 2016-05-01 | 2017-02-16 |
| NCT02718755 | Hematologic Malignancy | Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: Cytarabine|Drug: Erwinase | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|Jazz Pharmaceuticals | Phase 2 | 2016-12-01 | 2016-09-19 |
| NCT02926586 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia|Core-Binding Factor | Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: Cytarabine | Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine | Phase 4 | 2016-07-01 | 2016-10-05 |
| NCT02083250 | Leukemia | Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: Clofarabine|Drug: Busulfan|Drug: SAHA|Procedure: Stem Cell Infusion (SCT)|Drug: Thymoglobulin | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | Phase 1 | 2014-03-01 | 2016-09-06 |
| NCT01366612 | Myeloid Malignancies|Acute Myelogenous Leukemia|Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia|Myeloproliferative Disorders|Myelodysplastic Syndrome | Drug: Fludarabine and Busulfan plus/minus Total Body Irradiation (low dose)|Drug: Fludarabine and Busulfan + Low Dose Total Body Irradiation (LD TBI) | Hackensack University Medical Center | Phase 3 | 2010-06-01 | 2015-08-21 |
| NCT02514083 | CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia)|SLL (Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma) | Drug: Ibrutinib|Drug: Fludarabine | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) | Phase 2 | 2015-07-28 | 2017-01-24 |
| NCT03016988 | Mantle Cell Lymphoma | Drug: Bortezomib|Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: Cytarabine | Tingbo Liu|Union hospital of Fujian Medical University|Fujian Medical University | Phase 2 | 2017-01-01 | 2017-01-09 |
| NCT02629809 | Leukemia|Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Drug: Obinutuzumab|Drug: Fludarabine|Drug: Cyclophosphamide|Drug: Ibrutinib|Drug: Allopurinol|Drug: Valacyclovir | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|Genentech, Inc.|Pharmacyclics LLC. | Phase 2 | 2016-03-01 | 2017-03-03 |
| NCT00472329 | Graft Failure | Procedure: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell graft using an allogeneic SCT HLA-Identical or non-identical family donor or unrelated donors|Drug: fludarabine|Procedure: TBI | Colorado Blood Cancer Institute | Phase 2 | 2007-03-01 | 2014-06-26 |
| NCT01131169 | Multiple Myeloma | Drug: busulfan, melphalan and fludarabine|Drug: busulfan, melphalan and fludarabine | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center|Otsuka America Pharmaceutical|Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research | Phase 2 | 2010-05-01 | 2017-01-06 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们