-
生物活性
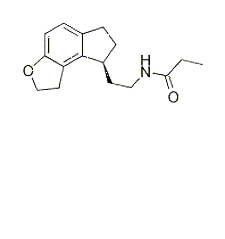
Ramelteon is a novel melatonin receptor agonist for human MT1 and MT2 receptors and chick forebrain melatonin receptors with Ki of 14 pM, 112 pM and 23.1 pM, respectively.
Activitiesfor melatonin receptor of Ramelteon[1]
Inhibitionof forskolin-induced cAMP production[1]

-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
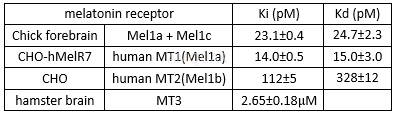
High-affinity melatonin receptor binding assays[1]
For the human MT1 receptor binding assay,cDNA encoding the human MT1 gene was introduced into Chinese hamster ovary(CHO) cells. A cell line stably expressing MT1 receptors (CHO-hMelR7) was selectedand cultured in Eagle’s Minimum Essential Medium-α (MEM-α)supplemented with 10% dialyzed fetal bovine serum (dFBS) under a 5% CO2/95%air atmosphere. Cells were harvested at confluence in Ca2+–Mg2+ free Hanks’ balanced salt solution containing 5mM EDTA and collected bycentrifugation. Cells were homogenized in ice-cold 50mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.7at 25oC), washed twice, pelleted, and stored at -30oCuntil the binding assays were conducted. Test compound and 40pM 2-[125I]melatonin were mixed with the thawed homogenate in a total volume of 1mL andincubated at 25oC for 150min. The reaction was terminated byaddition of 3mL of ice cold buffer followed by vacuum filtration on a Whatman GF/B.The filter was washed twice and radioactivity was counted by a γ-counter.Nonspecific binding was defined as the binding in the presence of 10mM melatonin.
For the human MT2 receptor binding assay,CHO cells were transfected with a pCMV-human MT2 receptor expression vectorusing LipofectAMINE reagent. A cell line stably expressing MT2 receptors wasselected and cultured in MEM-α supplemented with 10% FBS and 300 mg/mL geneticin under a 5% CO2/95%air atmosphereCells expressing MT2 receptors were harvested at confluence inDulbecco’s Phosphate-Buffered Saline and collected by centrifugation. Cellswere homogenized in ice-cold 50mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.6 at 25oC), washedtwice, pelleted, and stored at -80oC until the binding assays wereconducted. Test compound was mixed with the thawed homogenate and 280pM 2-[125I]melatonin in a total volume of 1 mL and incubated at 25oC for 150min. The reaction was terminated by addition of 3mL of ice-cold buffer followedby vacuum filtration on a Whatman GF/B. The filter was washed twice andradioactivity was counted by a γ-counter. Nonspecific binding was defined as the binding in thepresence of 100μM melatonin.
The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) wascalculated using the nonlinear logistic regression analysis. The dissociationconstant of the compound for the receptor (Ki) was calculated using followingequation: Ki=IC50/(1+L/Kd)
where L and Kd represent the concentrationand the dissociation constant of 2-[125I] melatonin in the binding assay,respectively.
-
细胞实验
Reagents[2]
Ramelteon, melatonin, 17β-estradioland the melatonin receptor antagonist luzindole (N-acetyl-2-benzytryptamine)were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and further diluted in culturemedium.
Celllines and cell culture
HHUA and the ER-negative human uterineendometrial cancer cell line SNG-II were maintained as monolayers in NutrientMixture F-12 Ham containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1%penicillin–streptomycin in 100 mm dishes at 37oC in a humidifiedatmosphere containing 5% CO2. Where indicated, the cells werecultured in phenol red-free RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% charcoal-stripped FBS.
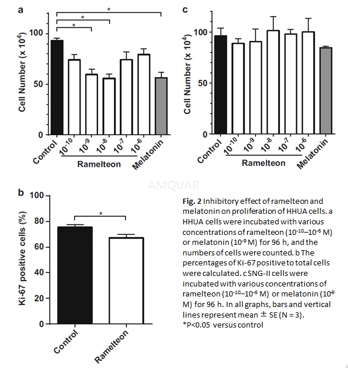
Cellproliferation assay
HHUA and SNG-II cells were cultured atdensities of 1x104/cm2 for 96 h in medium supplemented with ramelteonat various concentration or melatonin (1nM) as a positive control. The concentrationof the solvent DMSO in culture medium was kept constant at 0.1μ M. Viable cells were determined by trypan blue staining. In some experiments,17β-estradiol (0.1nM) or luzindole (5μM) was addedto the culture medium, followed by the addition of ramelteon (10μM).After incubation for96 h, the viable cells were counted.
-
动物实验
Animals[3]
Fabp3−/− mice on a C57BL/6 genetic wereused. Adult male mice (8–13weeks old) were used in all experiments. Animalswere housed under conditions of constant temperature (23 ± 1 °C) and humidity(55 ± 5%), in a 12-h light and dark cycle (light; 9–21 h). Animals were allowedto take food and drink water freely.
DrugAdministration
Ramelteon was dissolved in 0.5%carboxymethylcellulose (CMC). At 6 weeks of age, mice were orally administeredramelteon (0.1 or 1.0mg/ kg) once daily until the end of the experiment (atleast 2 weeks). In some cases, mice were treated with the melatonin receptorantagonist luzindole (2.5 mg/kg, i.p) 30 min before ramelteon administration. Wild-type(WT) mice were treated with the same volume of 0.5% CMC, ramelteon (1.0 mg/kg,p.o.), or luzindole (2.5 mg/kg, i.p.). Melatonin (0.1 mg/kg, p.o.) was suspendedin 0.5% CMC and administered to animals on the same schedule as ramelteon.
For behavioral analysis, we designed an experimentto decrease stress effects. (1) Group I was subjected to Y-maze and novelobject recognition tasks at 8 weeks old [WT treated with vehicle n = 6,ramelteon (1.0 mg/kg, p.o.) n = 9, luzindole (2.5 mg/kg, i.p.) n = 5; Fabp3−/−treated with vehicle n = 9, melatonin (0.1 mg/kg, p.o.) n = 5, ramelteon (0.1mg/kg, p.o.) n = 6, ramelteon (1.0 mg/kg, p.o.) n = 7, ramelteon (1.0 mg/kg, p.o.)+ luzindole (2.5 mg/kg, i.p.) n = 4].
Y-MazeTask
Spontaneous alternation behavior wasassessed using a Y-maze task. Briefly, a mouse was placed at the end of one armand then allowed to move freely through the maze during an 8-min period. Alternationwas defined as entries into all three arms on consecutive choices. The maximum numberof alternations was defined as the total number of arms entered minus two, andthe percentage of alternations was calculated as actual alternations/maximum alternationsx100. The total number of arms entered during the session was also determined.

-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Kato K, Hirai K, Nishiyama K, et al. Neurochemical properties of ramelteon (TAK-375), a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48(2):301-310.
[more]
分子式
C16H21NO2 |
分子量
259.34 |
CAS号
196597-26-9 |
储存方式
﹣20 ℃冷藏长期储存。冰袋运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
≥50 mg/mL |
Water
<1 mg/mL |
Ethanol
≥50 mg/mL |
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
| NCT Number | Conditions | Interventions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases | Start Date | Last Updated |
| NCT02669082 | Insomnia|Major Depressive Disorder | Drug: Ramelteon | Takeda | Phase 4 | 2017-02-01 | 2017-02-24 |
| NCT03091738 | Cirrhosis | Drug: Ramelteon Pill | Virginia Commonwealth University | Phase 4 | 2017-02-01 | 2017-03-21 |
| NCT01128582 | Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease|Chronic Insomnia | Drug: Rozerem (ramelteon)|Drug: placebo | Southern Arizona VA Health Care System | Phase 3 | 2009-03-01 | 2011-05-11 |
| NCT00914862 | Insomnia | Drug: Ramelteon | Takeda | Phase 1 | 2009-11-01 | 2012-03-07 |
| NCT00671632 | Drug Abuse | Drug: Ramelteon, triazolam, and placebo (56 possible combinations total) | Takeda | Phase 2 | 2003-06-01 | 2012-02-27 |
| NCT01048242 | Insomnia|Obstructive Sleep Apnea | Drug: rozerem|Drug: Placebo | University of Pennsylvania|Takeda | Phase 3 | 2006-07-01 | 2010-01-11 |
| NCT01677182 | Bipolar Disorder | Drug: Ramelteon|Drug: Placebo | Takeda | Phase 3 | 2012-08-01 | 2016-02-16 |
| NCT01467700 | Acute Depressive Episode | Drug: Ramelteon SL|Drug: Placebo | Takeda | Phase 3 | 2011-12-01 | 2016-04-08 |
| NCT00462254 | Parkinson's Disease | Drug: ROZEREM|Drug: Ramelteon | Southern California Institute for Research and Education | Phase 4 | 2007-06-01 | 2010-11-10 |
| NCT00316992 | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | Drug: Ramelteon and Placebo | Takeda | Phase 4 | 2006-04-01 | 2010-05-31 |
| NCT00247390 | Chronic Insomnia | Drug: Ramelteon|Drug: Placebo | Takeda | Phase 3 | 2005-07-01 | 2010-06-02 |
| NCT00568789 | Insomnia | Drug: Ramelteon, zolpidem and placebo | Takeda | Phase 4 | 2006-06-01 | 2012-02-27 |
| NCT00915135 | Chronic Insomnia | Drug: Ramelteon and Placebo (25 possible combinations total) | Takeda | Phase 2 | 2002-05-01 | 2010-05-31 |
| NCT02058992 | Insomnia | Drug: Ramelteon | Takeda | | 2010-07-01 | 2016-06-02 |
| NCT00391755 | Migraine Headache | Drug: ramelteon | Charlottesville Neuroscience|Takeda Pharmaceuticals North America, Inc. | Phase 4 | 2006-10-01 | 2012-02-08 |
| NCT00746239 | Panic Disorder|Insomnia | Drug: Placebo and Escitalopram|Drug: Ramelteon and Escitalopram | Penn State University|Takeda Pharmaceuticals North America, Inc. | | 2008-08-01 | 2015-09-14 |
| NCT00595075 | Healthy | Drug: Ramelteon|Drug: placebo | Brigham and Women's Hospital|Takeda | | 2007-12-01 | 2012-10-24 |
| NCT02840591 | Delirium | Drug: Ramelteon|Drug: Citicoline | University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center | Phase 4 | 2016-07-01 | 2016-07-20 |
| NCT02153086 | Drug: Ramelteon | Takeda | All | | 2014-06-01 | 2016-08-01 |
| NCT02564939 | Delirium | Drug: ramelteon|Drug: Placebo | Hartford Hospital | Phase 4 | 2017-02-01 | 2017-02-22 |
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们