-
生物活性
Ipilimumab (MDX-010), a humanized monoclonalantibody against CTLA-4, causes enhanced T-cell reaction, antitumor response,and significant improvement of the overall survival of patients with metastaticmelanoma.
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
-
细胞实验
Cell lines[1]
The human Burkitt’s lymphoma cell line(Daudi) and human pancreatic cancer cell line (COLO356/FG) were maintained inRPMI-1640 or DMEM culture media, respectively, supplemented with 10% fetal bovineserum (FBS), 2 mM L-glutamine, 50 IU/mL penicillin and 50μg/mL streptomycin.
Generationof ATC
PBMC for ATC expansion were obtained fromhealthy volunteers and leukapheresis samples from GI patients which werecryopreserved prior to immunotherapy. T cells in the PBMC were activated by 20ng/mL of anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (OKT3) and expanded with 100 IU/mL ofInterleukin-2 (IL-2) in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 50units/mL penicillin and 50 μg/mL streptomycin (complete RPMI-1640) for 14 daysat 37°C with5% CO2. At the initiation of culture, ipilimumab wasadded only once to the cultures at various concentrations (0, 0.5, 5.0, and 50μg/mL). Cultures were fed every 2 to 3 days and maintained at a concentrationof 1x106 cells/ mL. IL-2 was added at every feeding at 100 IU/mL.
Productionof bispecific antibodies and arming of ATC
Bispecific antibodies (BiAbs) were producedby chemical heteroconjugation of OKT3 and Rituxan (a humanized anti-CD20 IgG1)or Erbitux (a humanized anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) IgG1) asdescribed. ATC were armed with anti-OKT3 x anti-CD20 BiAb (CD20Bi) or anti-OKT3x anti-EGFR BiAb (EGFRBi) using a previously optimized concentration (50 ng/106 ATC).
Cytotoxicity/51Crrelease assay
To target adherent cells, COLO356/FG cellswere plated in 96-well flat-bottom microtiter plates at 4x104 cells/well and allowed to adhere overnight. The cells were labeled with 51Crat 20 μCi/mL in the labeling media (50% FBS in complete RPMI-1640) for 5 hoursat 37°C, and washed with complete RPMI-1640 to remove unincorporated isotope.For non-adherent cell targeting, Daudi cells were labeled with 51Crat 100 μCi/106 cells in a 15 mL conical tube for 4 hours at 37 °C, washed with completeRPMI-1640, and plated in 96-well round-bottom microtiter plates at 1x104 cells/well. Effectors (unarmed ATC and aATC) were then added to achieve effector:target(E:T) ratios of 25:1 and 12.5:1. Cocultures were incubated for 4 hours (Daudi)or 18 hours (COLO356/FG) and the supernatant was collected for liquid scintillationcounting to quantitate the amount of released 51Cr. Percentcytotoxicity was calculated as follows: (experimental cpm – spontaneouscpm)/(maximum cpm – spontaneous cpm) × 100. Means and standard errors werecalculated from four to six replicates per sample.
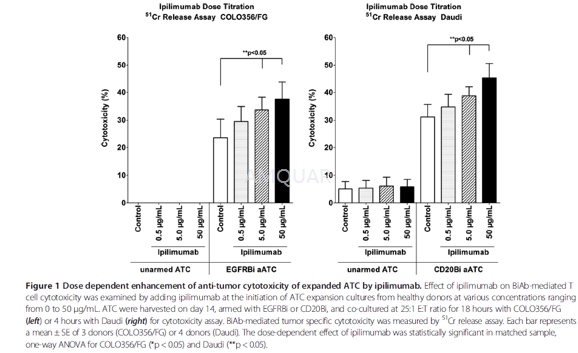
In Vitro Assays Using Human Lymphocytes[2]
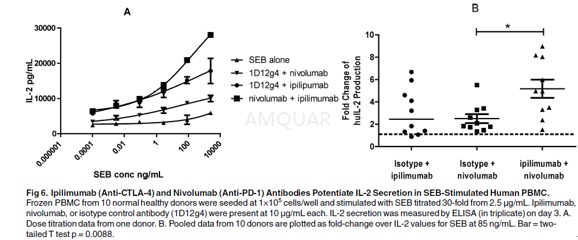
Frozen peripheral bloodmononuclear cells(PBMC) from normal healthy leukophoresis donors were seeded at 1×105 cells/well and stimulated with SEB serially diluted 30-fold from2.5μg/mL.Anti-CTLA-4 (ipilimumab), anti-PD-1 (nivolumab), or huIgG4 isotype control waspresent at a spike concentration of 10μg/mL. IL-2 secretion wasmeasured by ELISA on day 3.
Mixed lymphocyte response assays wereperformed by co-culturing 1×105 cells CD4+ T cells withallogeneicmonocyte-deriveddendritic cells (DC) at a ratio of 10:1 (T:DC) inflat-bottom96-well microtiter plates. CD4+ T cells and DC were incubated for 6 daysin the presence or absence of nivolumab titrated 1:10 from 50 mg/mL to 5 ng/mLalong with ipilimumab at 0, 5, or 50μg/mL. Culture supernatants wereharvested on day 5 for ELISA analysis of IFN-γ secretion.
To assess the potential of nivolumab or ipilimumab,alone or in combination, to induce nonspecific T cell activation, mAbs weremixed with samples of heparinized fresh human whole blood to measure cytokinerelease. After a 4-hour incubation at 37 oC, the cells were pelletedand the plasma fraction collected for measurement of IFN-γ,TNF-α, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10 using a cytokine cytometric bead arrayassay.Comparison was made to responses generated by anti-CD3 or isotype controlmAb treatment.
-
动物实验
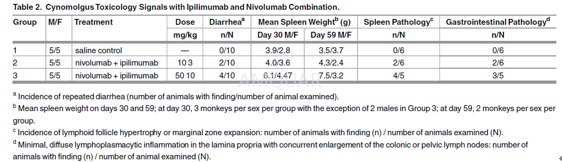
Cynomolgus Monkey Toxicity Study[2]
A 4-week study was conducted in cynomolgus monkeysto evaluate the toxicity of co-administered ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Thirty purpose-bred cynomolgus monkeys(5/sex/group) were assigned to 3 groups by a stratified randomization schemedesigned to achieve similar group mean body weights and the groups wererandomly assigned to treatment. The groups were dosed intravenously (IV) with 1)saline control, 2) nivolumab 10 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 3 mg/kg, or 3) nivolumab50 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 10 mg/kg, once weekly (days 1, 8, 15, and 22), for atotal of 4 doses. The animals were housed individually, but were commingleddaily to provide for environmental enrichment. Animals were fed PurinaCertified Primate Diet No. 5048, and fruits, vegetables, and other treats wereprovided for environmental enrichment. The animals were evaluated for changesin clinical signs daily and body weights were recorded weekly. Cardiovascular assessmentswere performed prior to study and on days 1 and 22. Clinical pathologyassessments were performed prior to study and on days 7, 28, and 58.
Seventeen monkeys (3/sex/group for Groups 1and 2, and 2 males/3 females for Group 3) were euthanized 8 days after the lastmAb dose, and 12 monkeys (2/sex/group) were euthanized on day 59. Animals wereeuthanized by exsanguination while under deep anesthesia induced with ketamineand Beuthanasia-D or equivalent. A full necropsy was conducted on all animals,with organs weighed and tissue collected, preserved, and processed formicroscopic and histologic evaluations.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Yano H, T. A., Tomaszewski EN, Choi M, Deol A, Lum LG, Ipilimumab augments antitumor activity of bispecific antibody-armed T cells. J Transl Med 2014, 12, 191.
[2] Selby, M. J.; Engelhardt, J. J.; Johnston, R. J.; Lu, L. S.; Han, M.; Thudium, K.; Yao, D.; Quigley, M.; Valle, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Cardarelli, P. M.; Blanset, D.; Korman, A. J., Preclinical Development of Ipilimumab and Nivolumab Combination Immunotherapy: Mouse Tumor Models, In Vitro Functional Studies, and Cynomolgus Macaque Toxicology. PLoS One 2016, 11 (9), e0161779.
分子式
|
分子量
|
CAS号
|
储存方式
-80 ℃长期储存。干冰运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
|
Water
|
Ethanol
|
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们



















