-
生物活性
Efalizumab, a recombinant humanizedmonoclonal IgG1 antibody directed against a subunit (CD11a) of leukocytefunction-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), inhibits the T cell activation,migration and adhesion to keratinocytes.
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
-
细胞实验
T cell activation assays[1]
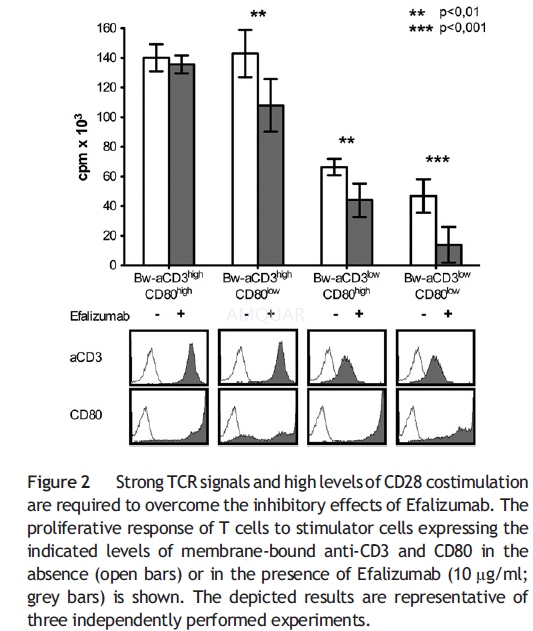
The generation and use of T cell stimulatorcells, derived from the murine thymoma cell line Bw5147 (Bw), expressingmembrane-bound anti-CD3 single chain Ab and human costimulatory molecules.Human T cells (1×105/well) and irradiated stimulator cells (2×104/well)were co-cultured in flatbottom 96-well culture plates for 72 h. Efalizumab ormurine mAbs were added at indicated concentrations at the initiation of T cell stimulationexperiments unless indicated otherwise. In some experiments, Interleukin-2 wasadded at the indicated concentrations.
For T cell activation assays usingimmobilized CD3 antibodies in conjunction with immobilized Efalizumab orICAM-Ig, 96-well ELISA plates were coated o/n at 4 °C with goat-anti-mouse IgG2a-specificAbs (3 μg/ml) and 10 μg/ml goat-anti-human IgG-Fcγ-specific Abs. Plates werewashed and antibodies to CD3 and ICAM-Ig or Efalizumab were added as indicated.For T cell proliferation assays with immobilized anti- CD3 mAb with or withoutanti-CD28 mAb, 96-well ELISA plates were coated with anti-CD3 mAb (1 μg/ml)alone or in combination with CD28 mAb (2 μg/ml) diluted in IMDM overnight at 4°C. For all T cell activation assays using immobilized antibodies, T cells wereadded after a final washing step at 1×105/well and cultured for 72h.
For mixed-lymphocyte reaction, allogeneic Tcells (1×105/well) were co-cultured with immature or LPS maturedmonocyte-derived (md) DC and Efalizumab and Abatacept were added at theindicated concentrations.
T cell proliferation was assessed bymeasuring the uptake of methyl-3[H]thymidine, which was presentduring the last 18 h of the assays. All T cell proliferation assays were donein triplicates, and means and SD are shown.
-
动物实验
Animals[2]
Eighty specific pathogen-free male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 240-290g were housed in pathogen-free laboratory for 72hwith free access to water and food. The rats were randomized into four groups:lung-protective ventilation group (LV) (n=20), injurious ventilation group (HV)(n=20), HV+human IgG treated group (n=20) and HV+efalizumab-treated group(n=20). Rats were sacrificed at indicated time points after ALI induction anddifferent administration.
MechanicalVentilation
Rats received efalizumab (2.5 mg/kg,dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS)) or human IgG protein (2.5 mg/kg)via tail vein injection. Thirty minutes later, rats were anesthetized byintraperitoneal injection of thiopental (37 mg/kg). Thiopental was chosen asthe anesthetic agent because it is slowly metabolized in rodents. The dose thatwe used ensures a profound anesthesia for at least 4 h. A tracheostomy wasperformed, and each animal was injected with succinylcholine (5 mg/kg) via thedorsal penile vein, after which the animal was ventilated with a rodent volume ventilator.Two ventilation modalities were used, for 2h each, as follows: (1) healthcontrol, with low VT ventilation (7 ml/kg VT and 3 cm H2O positive end-expiratorypressure [PEEP], 40 breaths/min) (LV group) and (2) an injurious strategy, usinga high VT and no PEEP (42 ml/kg VT, zero end-expiratory volume [ZEEP], 40 breaths/min)(HV group). Then rats were killed by an intravenous injection of thiopental atthe end of the mechanical ventilation period, the thorax was opened, and theblood was sampled by cardiac puncture. Simultaneously, three BAL procedures wereperformed, each with 2 ml of normal saline. The retrieved fluid and the bloodwere centrifuged (2,000 g, for 10 min), and the supernatant and plasma werestored for further processing. The survival after mechanical ventilation wasassessed and the cumulative survival curve was depicted using the Kaplan-Meiermethod.
HistopathologicAnalysis
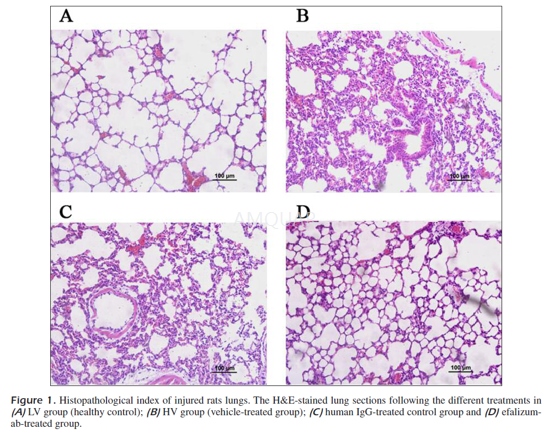
Following sacrifice, the whole left lowerlobe of the lung was fixed in a 4% formaldehyde neutral buffer solution for 24hours, dehydrated in a graded ethanol series, embedded in paraffin, and slicedat 5 m. Paraffin sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE) forhistopathological analysis.
LungWet/Dry Weight Ratio
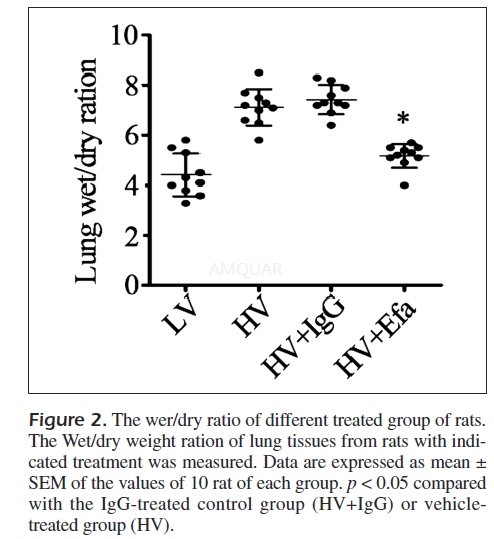
The superior lobe of the right lung was cleansedand weighed to obtain the wet weight, and was then placed in an oven at 80°Cfor 48h for measurement of the dry weight. The ratio of the wet weight to dryweight was calculated to assess the tissue edema. The experiment was repeated threetimes and results were shown with the mean value.
BtonchoalveolarLavage (BAL) Examination
The trachea was exposed and cannulated witha catheter. The left lung was lavaged for 4 times with sterile phosphatebuffered saline (PBS) in a volume of 0.5 ml/wash. The fluid recovered after lavagewas greater than 90% on average. The BAL fluid (BALF) was centrifuged at 2000rpm for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was stored at –80°C for cytokine andprotein analysis, while the cell pellet was resuspended in PBS for counting theneutrophils.
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Kuschei, W. M.; Leitner, J.; Majdic, O.; Pickl, W. F.; Zlabinger, G. J.; Grabmeier-Pfistershammer, K.; Steinberger, P., Costimulatory signals potently modulate the T cell inhibitory capacity of the therapeutic CD11a antibody Efalizumab. Clin Immunol 2011, 139 (2), 199-207.
[2] Pan WZ, S. C., Tian M, Yu JG, Anti-CD11c antibody, Efalizumab attenuate ventilator-induced lung injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014, 18 (15), 2182-90.
分子式
|
分子量
|
CAS号
|
储存方式
-80 ℃长期储存。干冰运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
|
Water
|
Ethanol
|
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们



















