-
生物活性
Daclizumab (daclizumab high-yield process) is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to the α-subunit(CD25) of the interleukin-2 receptor and favorably modulates the immune environmentin multiple sclerosis (MS).
Daclizumabbinds to CD25 with a Kd value of 4.5nM.[1]
Daclizumabinhibits IL-2 dependent proliferation of KIT225/K6 cells in vitro with an IC50of 3.14nM.[1]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
Plasmon resonance binding characterization usingsurface plasmon resonance[1]
Antibody binding properties werecharacterized to determine rate constants (ka and kd) and affinity constant(KD) for the binding interaction against soluble, recombinant human IL-2Rα (CD25)using Biacore technology. Each antibody material was immobilized on the chipsurface using primary amine covalent coupling chemistry. Recombinant CD25 was injectedat various concentrations in duplicate and reference surface for 2 minutesusing an automated method. The binding data was corrected using a referenceflow cell and buffer blank. The assay was replicated using a newly preparedsensor surface, and the binding data was then fit with BIAevaluation softwareusing a bivalent model to obtain the equilibrium constants for kinetic evaluation.
-
细胞实验
Cell culture and isolation of effector cells[1]
Relative antibody biological potencies fordirect inhibition of IL-2-dependent high-affinity IL-2 receptor-mediatedproliferation were determined using a cell-based method that evaluated effectsof titrated antibody concentrations on the proliferation of the human leukemiacell line KIT225/K6.28 PBMCs were isolated with Ficoll-PaqueTM Plus densitygradients and used as the effector cells in ADCC assays. In additional ADCCexperiments, monocyte and NK cells were removed from PBMC cultures usingEasySepTM Human CD34 Positive Selection Kits for CD14 and CD56, respectively,and using the manufacturer’s protocol for the RobosepTM Automated CellSeparation System. Target cell depletion was found to be greater than 95% byflow cytometric analysis. All blood was obtained from informed consentedhealthy volunteers and no genotyping of individual donors was performed.
51Cr-labeling of target cells
KIT225/K6 cells were grown in RPMI 1640complete medium (10% heat inactivated fetal bovine serum plus supplements). KIT225/K6cells were suspended in 0.5 mL of Assay Medium (RPMI 1640, 10% heat inactivatedfetal bovine serumplus supplements) at a final concentration of 2 x107 cells/mL, and labeled with 500μCi of 51Cr (50μCi/106 cells) by incubating at 37oC in a water bath for 1 hr withoccasional mixing. Labeled cells were washed 4 times with 12 mL of AssayMedium. The efficiency of target labeling was evaluated using the Beckman Gamma5500B counter and considered acceptable if there was an activity of at least20,000 cpm/105 cells. Labeled target cells were suspended at a celldensity of 2.5 x 105 cells/mL in Assay Medium, or 5.0 x105 cells/mL in CDC Assay Medium, as appropriate.
Complement-dependentcytotoxicity assay
Antibodies were diluted serially in CDC AssayMedium containing RPMI 1640, 0.1% BSA and 10 mM HEPES. 50μLof 51Cr-labeled target cells (25,000cells/well) was added to the wellsof amicrotiter U-bottom 96-well plate, and then a volume of 50μlof serial dilutions of test antibodies was added. 25μl of 8%Triton X-100 and25μl of CDC Assay Medium were added to maximum-release wells and 50 μlof CDC Assay Medium was added to spontaneous release wells (quadruplicate). 50μlof 1/3 dilution of human pooled serum was added to the reference and testsample wells. 50ml of 1/3 dilution of heat inactivated (30 min at 56oC)human pooled serum was added to a complement-independent control, maximum release,and spontaneous release wells. The optimal human pooled serum concentration waspre-established by identifying the concentration at which the specific activitywas maximal while the non-specific activity was minimal. Assay plates were incubatedfor 2 hr at 37oC in a 7.5% CO2 incubator and then spun at350 RCF for 5 minutes at room temperature. A volume of 75μlof supernatant was transferred tomini-tubes, and eachmini-tube was inserted intoa scintillation vial and counted for 1 minute in a Beckman Gamma 5500B counter,or equivalent. Pooled human serum was obtained from Quidel Corporation orhealthy volunteers using venipuncture and standard techniques.
The positive control antibody for CDCactivity was the humanized IgG1/k antibody, Hu#4, that has binding specificity forpan HLA-DR. The negative control antibody for both CDC and ADCC activity wasthe humanized IgG1/k antibody HuFd79 that has binding specificity for an HSVviral antigen. Values reported as Percent Specific Lysis were derived using thefollowing formula: Percent Specific Lysis = ((Antibody treatment counts perminute (CPM) – Spontaneous CPM) / (Maximum CPM – Spontaneous CPM)) x 100.
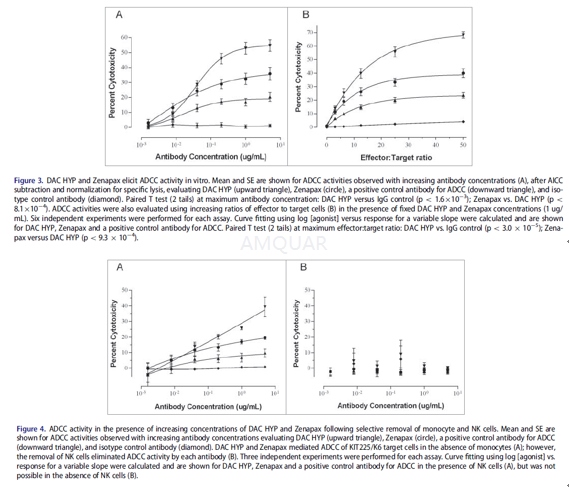
Antibody-dependentcell-mediated cytotoxicity assay
51Cr-labeledKIT225/K6 cells (12,500 cells/well) were pre-incubated with a fixedconcentration of 1μg/mL mAb (for the variable effector to target [E:T] ratio format) orvarious doses (5, 1, 0.2, 0.04, 0.008, and 0.0016 μg/mL) of mAbs(for the variable antibody concentration format) for 30 minutes at 4oCin V-bottom96- well plates in a volume of 100μL of AssayMedium. Control cells were incubated with Assay Medium alone (no mAb) for subsequentdetermination of the spontaneous and maximum 51Cr release, as wellas antibody-independent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (AICC). PBMC (effectors)were diluted serially in Assay Medium, in a separate 96-well polypropyleneplate, yielding concentrations of 6.25 x 105 cells/100μL,3.13x 105 cells/100μL, 1.56 x 105 cells/100μL, 7.81x 104 cells/100μL, 3.91 x 104 cells/100μL. 100μLper well of PBMC suspension was transferred to the variable E:T ratio assayplate containing 51Cr-labeled KIT225/K6 + 1μg/mL mAbs,yielding E:T ratios of 50:1, 25:1, 12.5:1, 6.25:1 and 3.13:1. To the variableantibody concentration assay plate, PBMCs were diluted to 3.13 £ 106 cells/100μLand100μL per well was added to assay wells. 100μL per well ofAssay Medium alone (no effector) was added to 51Cr-labeled KIT225/K6C mAbs, to determine spontaneous and maximum release of 51Cr. Theassay plates were spun at 50 RCF for 2 minutes and incubated at 37oCin a 7.5% CO2incubator for 4 hrs. Thirty minutes before the end ofthe 4-hr incubation, a volume of 25μL of 8% TritonX-100 was added tothe appropriate control wells to determine the maximum release of 51Crfrom target cells. The positive control antibody for ADCC activity was the humanizedIgG1/k antibody Hu1D10 that has binding specificity for the HLA-DR b chain.
Inhibitionof IL-2-dependent proliferation
Relative potencies of Zenapax and DAC HYPwere determined using the human KIT225/K6 cell line that requires IL-2 forproliferation. Antibody was titrated against a unit volume of cells in thepresence of IL-2 in a microtiter tissue culture plate and reduction of Alamarblue was determined using 530 nm excitation and 590 nm emission wavelengths.Potencies were determined by plotting the relative fluorescence units againstthe log10 of concentration values to produce sigmoidal curves and evaluatedusing a 4-parameter fit in SoftMax Pro 4.3 software.
-
动物实验
Mouse model of ATL[2]
The ATL cell population, MET-1, wasestablished from the peripheral blood of a patient with acute ATL, and thecells were maintained by serial transfer in NOD/SCID mice. MET-1 cells have adistinct phenotype elucidated by fluorescein-activated cell sorting analysis:CD3dim, CD4+/-, CD7-, CD20- andCD25+. The leukemia model was established by intraperitonealinjection of 1.5 x 107 MET-1 cells into NOD/SCID mice. The therapy experimentswere performed on these mice when their serum-soluble IL-2R-α (sIL-2R-α) levels were more than 1000 pg/mL, which occurs approximately 10 to14 days after tumor inoculation.
Definitionof the maximum tolerated dose
Before the initiation of the therapeuticstudies, the maximum tolerated dose of depsipeptide was determined in NOD/SCIDmice. Doses of 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mg depsipeptide per kilogram ofbody weight were administered intraperitoneally daily for 2 weeks. All mice inthe 2.0 mg/kg group died at day 7 and 80% of the mice in the 1.0 mg/kg groupdied at day 14. The mice in the 0.5, 0.25, and 0.125 mg/kg group were stillalive 6 months after depsipeptide injection. Therefore, a dose of 0.5 mg/kgevery other day for 14 days was chosen to use in the therapeutic trials; thisdose is consistent with what other researchers have used in mice.
Therapystudy
Therapeutic studies were performed in MET-1leukemia-bearing mice with serum surrogate tumor marker sIL-2R-α values of 1000 to 10 000 pg/mL in the small tumor burden trial and 10 000 to 25000 pg/mL in the large tumor burden trial. There were 5 groups in thetherapeutic trials. Group 1, the depsipeptide group, received intraperitonealinjections of 0.5mg depsipeptide/ kg body weight every other day for 2 weeks.Group 2, the immunotherapy (daclizumab) group, was given intravenous injectionsof 100μg daclizumab on days 0, 7, 14, and 21. Group 3, the combinationtherapy group, received a combined therapy of depsipeptide and daclizumab(dosing schedule as in group 1 plus group 2). Group 4 received 200μLof PBS weekly for 4 weeks and served as a control. Group 5, with no tumor andno therapy, served as a control for the natural death of NOD/SCID mouse. Therewere 13 mice per group in the small tumor burden therapeutic trial (sIL-2R-α,1000-10 000 pg/mL), and there were 8 mice per group in the large tumor burdentrial (sIL-2R-α, 10 000-25 000 pg/mL). The groups were randomly assigned and hadcomparable average levels of the surrogate tumor marker, sIL-2R-α,at the beginning of the experiments.
Monitoringof tumor growth
Measurements of the serum concentrations ofthe soluble IL-2R-α or soluble β2-microglobulin (β2μ) were performed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Theenzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed following the manufacturer’srecommendation.


-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Ganguly, B.; Balasa, B.; Efros, L.; Hinton, P. R.; Hartman, S.; Thakur, A.; Xiong, J. M.; Schmidt, B.; Robinson, R. R.; Sornasse, T.; Vexler, V.; Sheridan, J. P., The CD25-binding antibody Daclizumab High-Yield Process has a distinct glycosylation pattern and reduced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in comparison to Zenapax(R). MAbs 2016, 8 (7), 1417-1424.
[2] Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Ju, W.; Waldmann, T. A., Effective treatment of a murine model of adult T-cell leukemia using depsipeptide and its combination with unmodified daclizumab directed toward CD25. Blood 2009, 113 (6), 1287-93.
分子式
|
分子量
|
CAS号
|
储存方式
-80 ℃长期储存。干冰运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
|
Water
|
Ethanol
|
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们



















