-
生物活性
Atezolizumabbinds human and mouse PD-L1 with dissociation constants (Kd) of 0.43 and0.13nM, respectively.[1]
-
体外研究
-
体内研究
-
激酶实验
In Vitro Binding Assay[1]
In vitro binding of atezolizumab to CHO-hPD-L1,CHO, MDAMB231, SUM149, and 4T1 cells was determined by incubating 1μCi ofatezolizumab with 1 × 106cells for 1 h at 37 °C. The PD-L1 blockingwas performed by adding a 10-fold molar equivalent excess of the nonlabeledmAb. After incubation, cells were washed three times with cold PBS prior tocounting on an automated gamma counter. The study was performed in triplicate andrepeated three times.
-
细胞实验
Cells[2]
CaSki and HEK293 cell lines were maintainedin the MEM or RPMI-1640 culture media supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovineserum (FBS).
Preparationof DCs and CIKs
Separated from 70mL peripheral bloodsterilely collected from a healthy adult volunteer by using Ficoll-Paque, PBMCswere cultured in RPMI-1640 at 1 x 106 /mL supplemented with 10%(V/V) autologous serum. The obtained cells were subsequently transferred intoculture flasks and cultured for 2 h. Collected as the progenitor of CIKs,Nonadherent cells were resuspended at 1 x 106 cells/mL in RPMI-1640 mediumsupplemented with 10% human AB serum and cultured with rhIFN-γ (1000 UmL) and rhIL-2 (500 U/mL) as well as anti-CD3 antibody (10 mg/ mL)immobilized in culture flask. Half the amount of medium supplemented withrhIL-2 and rhIFN-γ was exchanged every 3 d. The remaining adherent cells were culturedin RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 40ng/mL rhGM-CSF and 40ng/mL rhIL-4. Thesupernatant was replaced with fresh medium containing rhGM-CSF and rhIL-4 every3 d. All cultures were incubated at 37 oC in 5% humidified CO2.After 7 d of culture, >80 % of the cells expressed characteristicDC-specific markers demonstrated by flow cytometric analysis. Then, the DCswere exposed to Ad-shSOCS1 at 100 MOI for 8 h. The transducted cells werewashed with PBS and pulsed with the HPVm16E7 protein at 25μg/mLin fresh culture medium for 6hrs (The recombinant adenovirus AdshSOCS1 andHPVm16E7 were prepared), followed by stimulation with TNF-α (10 ng/mL) for 24 h to develop mature DCs. The finally matured DCs wereco-cultured with CIKs at a ratio of 10:1 in CIK medium for 3 d to generate DCCIKs.
Invitro antitumor activity analysis
The in vitro cytotoxicity of the DCCIKsused as effector cells in the absence or presence of 5μg/mL MPDL3280Aagainst CaSki cells employed as target cells at a ratio of 10:1, 30:1 and 90:1was determined using a CCK8 kit. The effector and target cells were added to96-well plates and incubated for 24 h. The groups comprising a mixture of celltypes were the experimental groups, whereas the control groups contained onlyone cell type of the CaSki cells, DCCIKs or 1640 RPMI cultivating solution. TheCCK8 assay was performed in triplicate and optical density (OD) was read at 570nm. The cytotoxic activity was calculated as follows:
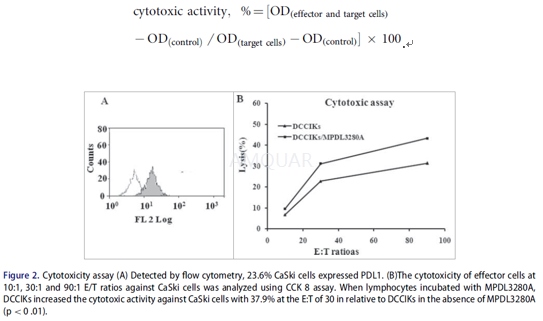
-
动物实验
Animals[2]
Female BALB/c mice weighing 16 to 22 g and 6to 8 weeks of age were raised under SPF circumstance.
Invivo antitumor assay
Xenografted tumor mouse models wereestablished by subcutaneous inoculation of 1x 106 CaSki cells into theright flank of female BALB/c mice. At day 7, all mice had palpable tumorsapproximately 100 mm3 were assigned to 4 groups: normal human IgGserved as control; DCCIKs; MPDL3280A (0.1 mg in 0.1mL PBS administeredintravenously); and DCCIKs in combination with 0.1mg MPDL3280A in 0.1mL PBS administeredi.v., 10 mice in each group. And therapeutic treatments were initiatedrespectively. Adoptive cell immunotherapy consisted of 2 intravenous transfusionof DCCIKs at d 7 and d 14 (1 x 107 cells per dose in a total volumeof 0.1 mL in the presence of o.1 mg control normal human IgG or MPDL3280A, respectively).For the treatment with Ab, 0.1mg MPDL3280A or normal human IgG as a control wasi.v. injected at the same time as adoptive cell immunotherapy was administered.The tumor volumes were recorded daily. And the tumor volume was calculated bythe following formula: (major axis x minor axis2) x 0.52. When thetumor volume reached ~4000 mm3, the tumor-bearing mice wereeuthanized to avoid unnecessary pain and recorded as dead.
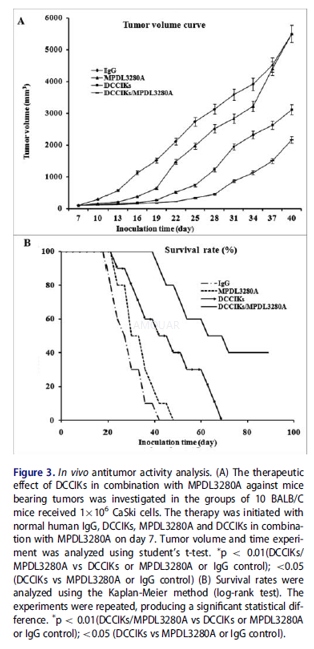
-
不同实验动物依据体表面积的等效剂量转换表(数据来源于FDA指南)
|  动物 A (mg/kg) = 动物 B (mg/kg)×动物 B的Km系数/动物 A的Km系数 |
|
例如,已知某工具药用于小鼠的剂量为88 mg/kg , 则用于大鼠的剂量换算方法:将88 mg/kg 乘以小鼠的Km系数(3),再除以大鼠的Km系数(6),得到该药物用于大鼠的等效剂量44 mg/kg。
-
参考文献
[1] Lesniak, W. G.; Chatterjee, S.; Gabrielson, M.; Lisok, A.; Wharram, B.; Pomper, M. G.; Nimmagadda, S., PD-L1 Detection in Tumors Using [(64)Cu]Atezolizumab with PET. Bioconjug Chem 2016, 27 (9), 2103-10.
[2] Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, X., Combining MPDL3280A with adoptive cell immunotherapy exerts better antitumor effects against cervical cancer. Bioengineered 2016, 1-7.
分子式
|
分子量
|
CAS号
|
储存方式
-80 ℃长期储存。干冰运输 |
溶剂(常温)
|
DMSO
|
Water
|
Ethanol
|
体内溶解度
-
Clinical Trial Information ( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov )
注:以上所有数据均来自公开文献,并不保证对所有实验均有效,数据仅供参考。
-
相关化合物库
-
使用AMQUAR产品发表文献后请联系我们


















