Ubiquitin
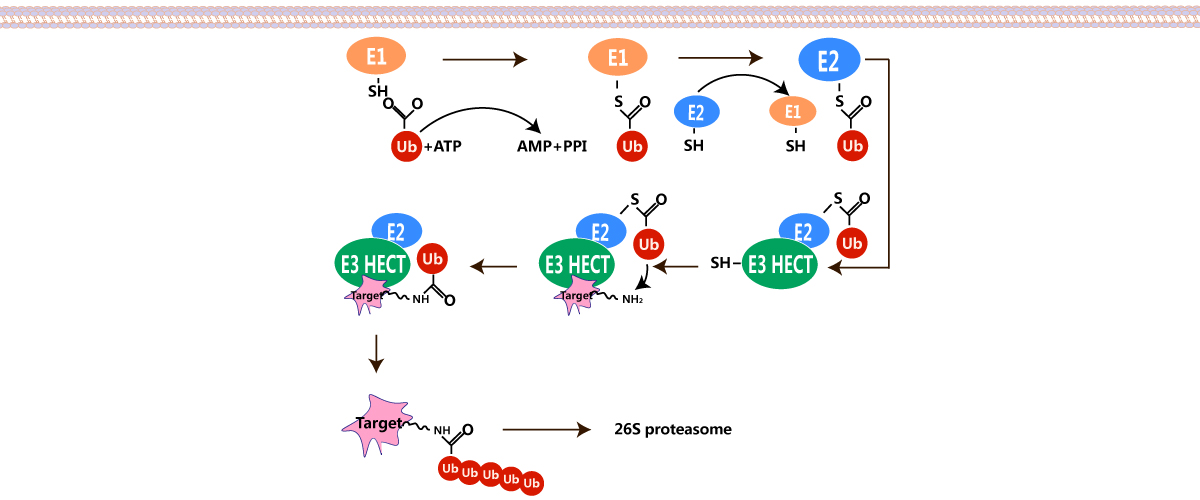
Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues (ubiquitously) of eukaryotic organisms.Ubiquitination (or ubiquitylation) is an enzymatic post-translational modification in which a ubiquitin protein is attached to a substrate protein.
The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination or ubiquitylation. Ubiquitination can affect proteins in many ways: it can signal for their degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitination is carried out in three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. Multi-monoubiquitination can mark transmembrane proteins for removal from membranes and fulfil several signalling roles within the cell.